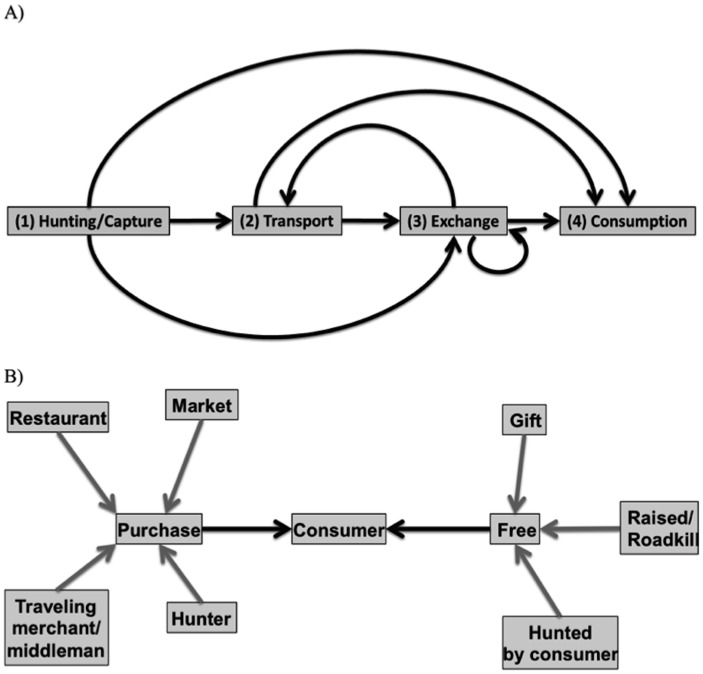
Fig 2. Conceptual commodity chain models (A) and the sources from which consumers procure wild meat (B).
The commodity chain (A) is not always linear and does not always include all actors; for example, in some cases, the consumer is also the hunter. In image (B) there are two tiers of arrows; the arrows that connect peripheral boxes to the “purchase” and “free” boxes represent direct quantities measured (black arrows) while the arrows connecting the “purchase” and “free” boxes to the consumer represent sums of the peripheral boxes of each type (gray arrows).