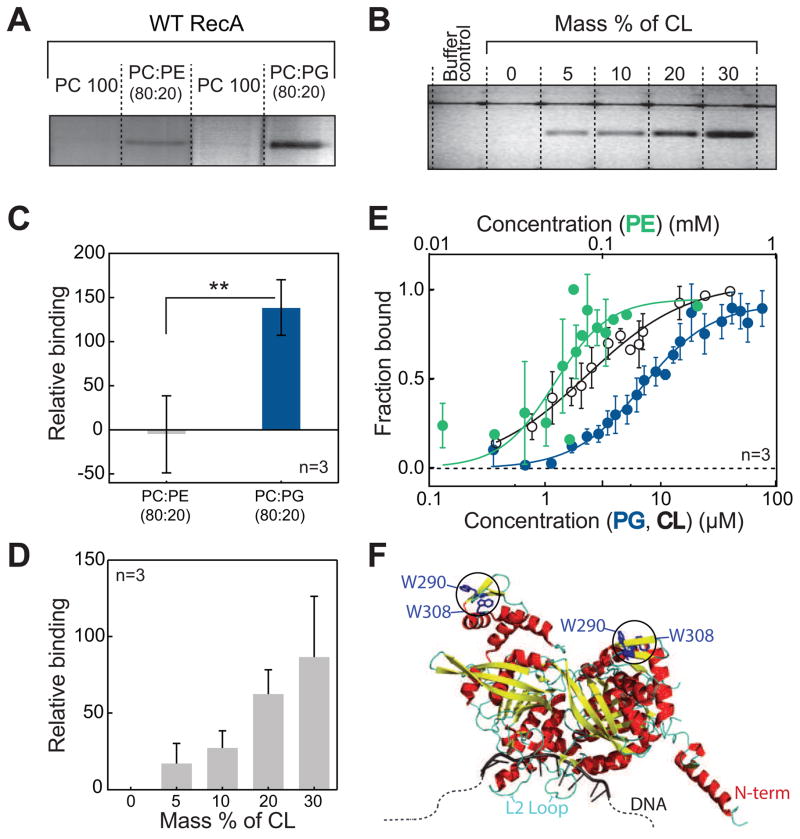
Figure 1. E. coli RecA interacts specifically and with high affinity to anionic phospholipids.
(A and C) Co-flotation assays of RecA with PE and PG demonstrate that RecA binds to anionic PLs with high affinity. ** p<0.05 indicates statistical significance calculated by a two-tailed t test. (B and D) The binding of RecA with CL increases proportionally with increasing CL concentration. (E) Langmuir binding isotherms of RecA with PE, PG, and CL demonstrate binding parameters as follows: PE (Kd = 52.9 ± 8.6 μM, Hill coefficient = 2.8 ± 1.1 and R2=0.7), PG (Kd = 6.9 ± 1.2 μM, Hill coefficient = 1.5 ± 0.3 and R2 = 0.93), and CL (Kd = 2.4 ± 0.4 μM, Hill coefficient = 1.0 ± 0.1 and R2 = 0.91). (F) Crystal structure (PDB ID 3CMU) of a dimer of RecA showing the position of the two Trp residues used to quantify binding affinities. All error bars indicate SD.