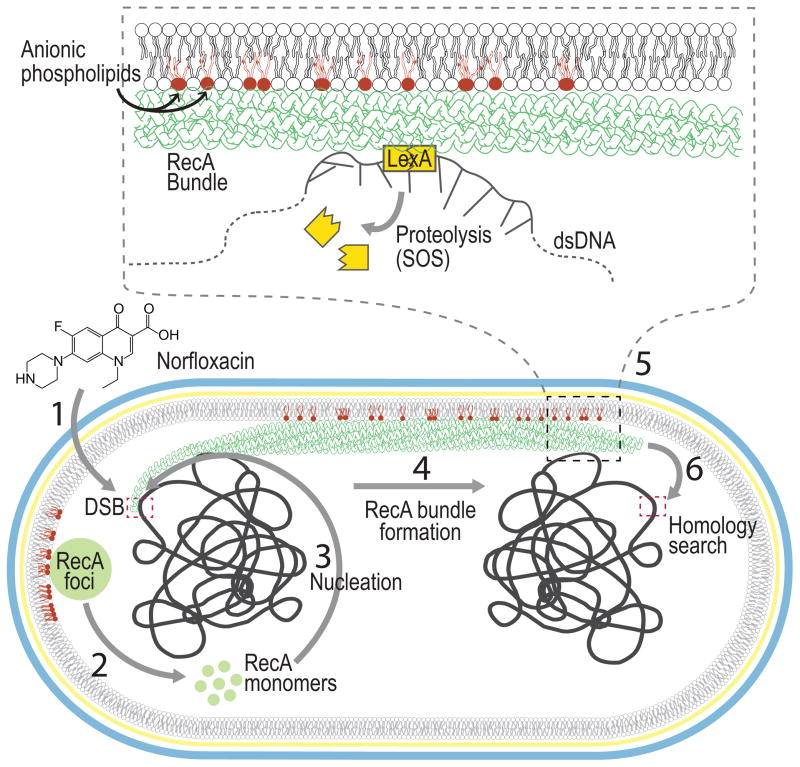
Figure 6. Model for the role of the inner membrane in RecA filament bundle formation.
(1) Norfloxacin treatment of E. coli cells produces double stranded breaks (DSBs). (2) RecA protein which undergoes exchange between the cytoplasm and RecA foci, (3) nucleates on the processed DSB due to its high affinity to ssDNA (4) and forms RecA bundles associated with the IM (6) which extend across the cell searching for homology. (5) At some point during this search for homology, contact between the RecA bundle and LexA facilitates the autocleavage of LexA leading to the SOS response. RecA bundles are a stylized version of those observed by electron microscopy (Yu and Egelman, 1992).