FIG 1.
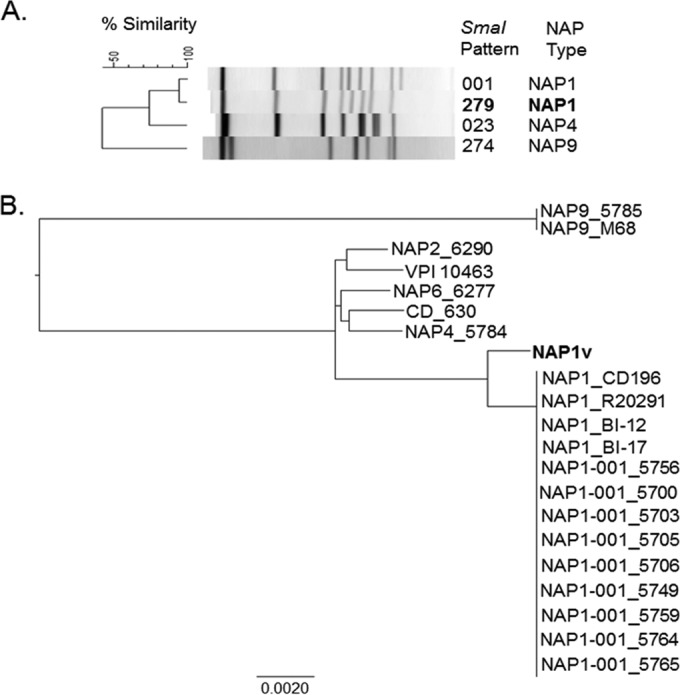
PFGE and core genome-based analysis of the phylogenetic relatedness of NAP1 strains analyzed. (A) Two different SmaI macrorestriction patterns were detected, 001 and 279. The variant NAP1 strain was allocated to the latter group, and thus, we named it NAP1V. NAP4 (TcdA+ TcdB+) and NAP9 (TcdA− TcdB+) strains were included in the dendrogram for comparative purposes. (B) A phylogenetic reconstruction based on core SNPs revealed that the NAP1V strain was more closely related to NAP1 reference strains and clinical isolates than to contemporary NAP2, NAP4, NAP6, and NAP9 clinical isolates (four-digit identifiers after the PFGE pattern) and to CD_630 and VPI 10463 strains. The genomes of reference NAP1/RT027 (CD196, R20291, B1-12, and BI17), NAP9/RT017 (M68), CD_630, and VPI 10463 strains were included in the analysis to validate the results of the PFGE typing method.
