Fig. 1.
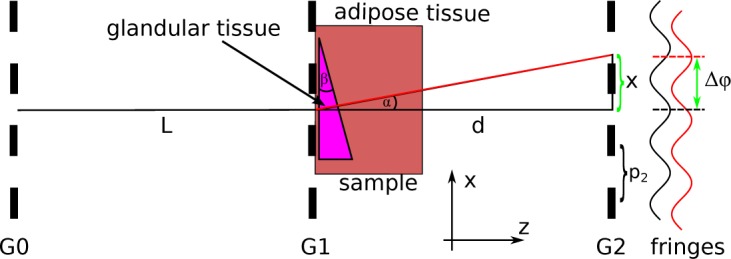
Principle of gbDPCi using a Talbot-Lau interferometer. The X-ray is refracted (from the black to red path) by the sample with height h(x) at a fixed angle α that is translated into a lateral shift x of the interference pattern. The shift x increases with increasing distance d. After the sampling with G2, this shift is translated into a phase shift of the stepping curve Δφ.
