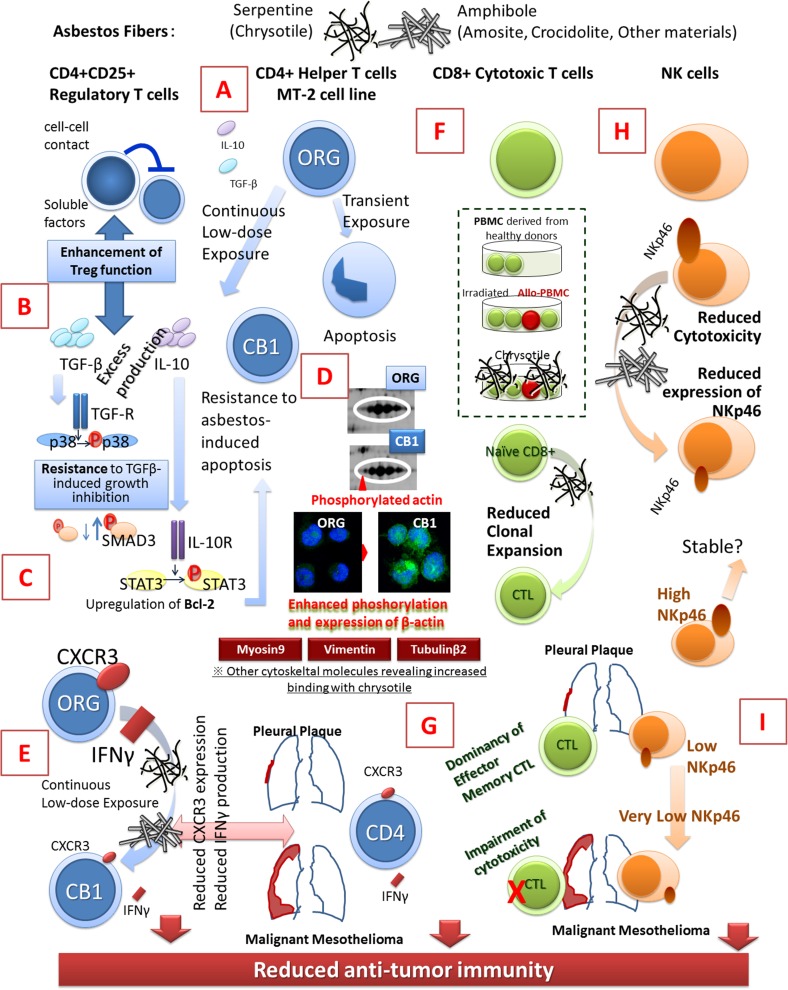
Fig. 1.
Schematic presentation showing the immunological effects of asbestos fibers on regulatory T cells, CD4+ helper T cells, CD8+ cytotoxic T and natural killer cells. ORG MT-2 original cell line, CB1 one of the sublines of the MT-2 cell line continuously exposed to chrysotile B asbestos, IL interleukin, TGF transforming growth factor, SMAD signal transducing adaptor proteins, STAT3 signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, R receptor, CXCR3 chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 3, IFN interferon, CTL cytotoxic T lymphocyte, PBMC peripheral blood mononuclear cells, NK natural killer. a Excess production of IL-10 and TGF-β in MT-2 subline (CB1) continuously exposed to asbestos, b resistance to TGF-β-induced growth inhibition in MT-2 subline (CB1), c acquisition of asbestos-induced apoptosis in MT-2 subline (CB1) via excess production of IL-10, phosphorylation of STAT3 subsequent overexpression of Bcl-2, d enhanced β-actin phosphorylation in MT-2 subline (CB1), e reduction of CXCR3 and IFN-γ-producibility inMT-2 subline (CB1) meaning reduction of anti-tumor immunity, f reduction of CTL clonal expansion in co-culture with asbestos, g aberrant CTL population and function in patients with pleural plaque (PP) or malignant mesothelioma (MM), h decrease of NKp46 activating receptor by asbestos exposure in NK cells and i progressive reduction of NKp46 in patients with PP–MM