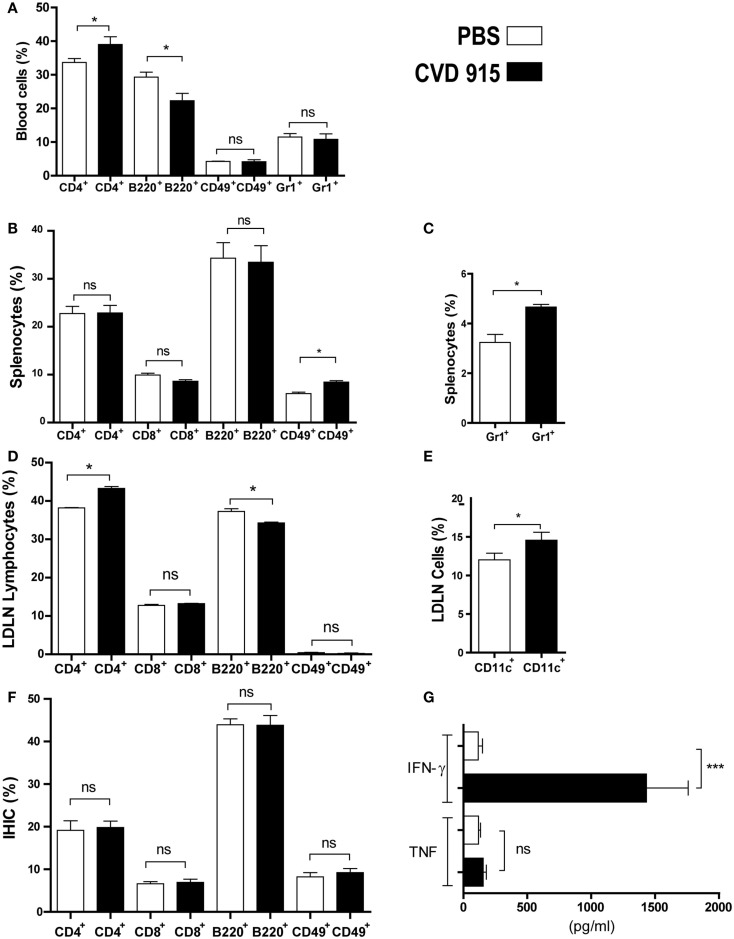
Figure 1.
Early immune response with IFN-γ production in liver of naive mice after oral Salmonella administration. BALB/c mice were immunized with CVD 915 via o.g. or PBS as a control. After 24 h, animals were sacrificed for sampling. (A–F) Cell phenotype of individual mice was analyzed by flow cytometry (n = 3–13). (A) Percentage of blood cells. (B) Percentage of splenic lymphocytes. (C) Percentage of splenic neutrophils. (D) Percentage of lymphocytes from liver-draining lymph nodes (LDLN). (A–D) *p < 0.05; ns, not statistically significant. Data are from one experiment representative of three to five. (E) Percentage of CD11c+ cells between LDLN cells, gated on DC region as defined in Section “Materials and Methods.” *p < 0.05. (F) Percentage of lymphocytes from intrahepatic immune cells (IHIC). ns, not statistically significant. (E,F) Data are from three experiments. (G) IFN-γ and TNF levels produced by IHIC measured by ELISA. The limits of detection were 30 and 4 pg/ml, respectively. ***p < 0.001; ns = not statistically significant (n = 9). Data are from two experiments.