Figure 4. Summary of intramitochondrial changes that occur during acclimatisation to extreme high altitude .
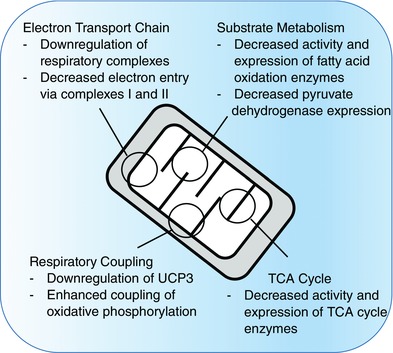
Studies at extreme high altitude have shown changes in enzyme activities and protein levels that suggest downregulation of electron transport chain (ETC) complexes, tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle enzymes and substrate oxidation enzymes, alongside decreased levels of uncoupling protein 3 (UCP3). High resolution respirometry of human muscle fibres at more moderate high altitude has shown that sustained hypoxia is associated with decreased electron entry into the ETC and improved mitochondrial efficiency.
