Fig. 6.
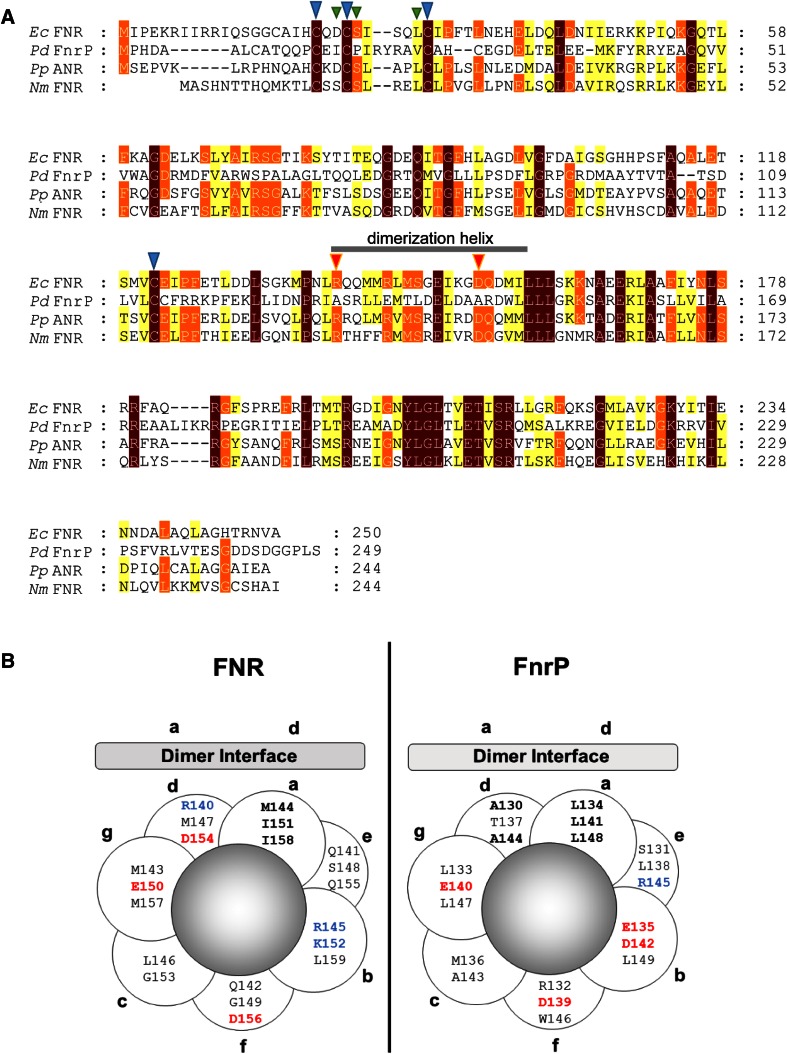
Sequence alignments of FNR proteins and comparison of the dimerization helixes of FNR and FnrP. a Sequence alignment of FNR proteins. The dimerization helix is indicated. Cluster-coordinating residues are indicated by blue arrowheads. Residues next to cluster-coordinating Cys residues that are important for controlling cluster reactivity are indicated by green arrowheads. Two key residues within the helix that are important for E. coli FNR association state, Arg140 and Asp154, are indicated by orange arrowheads. Proteins are E. coli FNR (EcFNR), Paracoccus denitrificans FnrP (PdFnrP), Pseudomonas aeruginosa FNR (PaNnrR) and Neisseria meningitidis FNR (NmCRP). The alignment was generated using Clustal Omega [53] and annotated using Genedoc [54]. b Helical wheel projection of the dimerization helix of a E. coli FNR and b P. denitrificans FnrP, assuming the standard 3.5 residues per turn for a coiled coil. Residues that when substituted by alanine result in a significantly altered activity in E. coli FNR, and predicted equivalents in FnrP, occupy positions a and d of the helical wheel. Adapted from Moore et al. [46]