Figure 5.
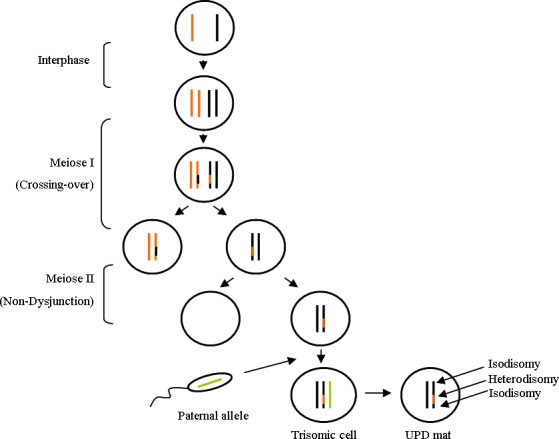
Mechanism of upd(14)mat in our patient: Meiosis I with double crossing‐over between homologous chromosomes 14, followed by Meiosis II with nondisjunction of sister chromatids, leading after fertilization to trisomic cells for chromosome 14. The elimination of the paternal copy of chromosome 14 is responsible for upd(14)mat in nontrisomic cells. Coexistence of proximal/distal isodisomy and central heterodisomy is the consequence of the double crossing‐over in Meiosis I.
