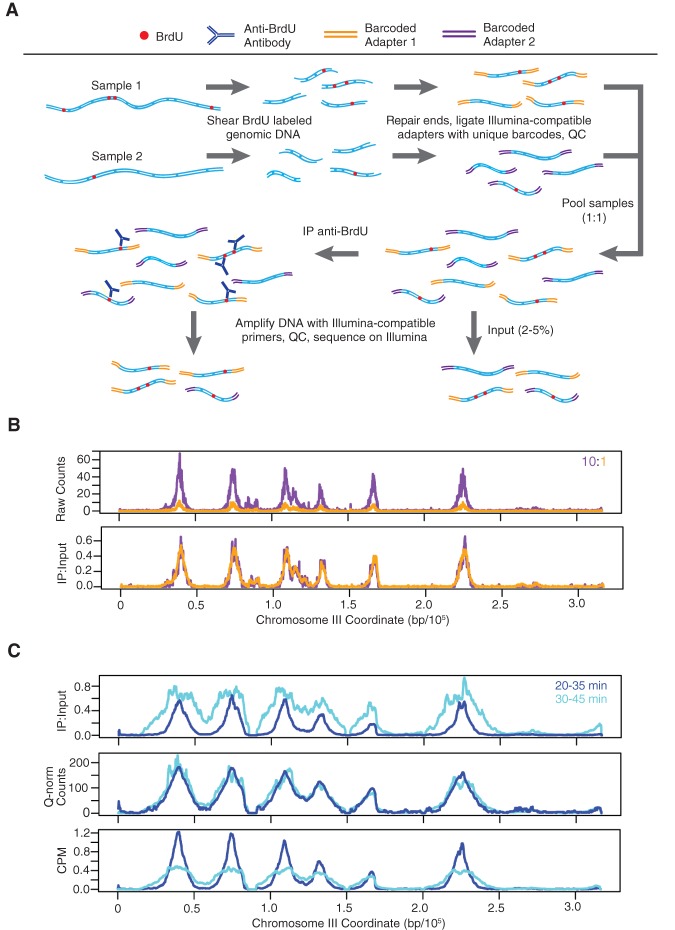
Figure 1.
Quantitative BrdU-IP-seq analysis. (A) Scheme of the method. BrdU-labeled genomic DNA from each sample is barcoded by end-ligation of Illumina-compatible linkers. Samples are pooled, a small fraction of this pool is set aside as “Input,” and the remainder is subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-BrdU antibody. The IP and Input samples are PCR-amplified with indexed primers and sequenced. IP sample reads are normalized against Input sample reads. (B) Validation of the method. A BrdU-labeled genomic DNA sample was split in two and each aliquot was uniquely barcoded. The distinctly barcoded samples were pooled at a ratio of 1:10 (color-keyed) and processed as above. IP results are shown raw and with normalization against the Input. (C) Comparison to CPM and Quantile normalization (Q-norm). JPy88 (WT) cells were synchronized in G1 phase with α-factor, released into S phase, and aliquots were incubated with BrdU for the indicated time intervals and harvested. The samples were processed as described for qBrdU-seq in A, and the IP sequence reads were analyzed by qBrdU-seq, CPM, or Quantile normalization and plotted as overlays of the time points.