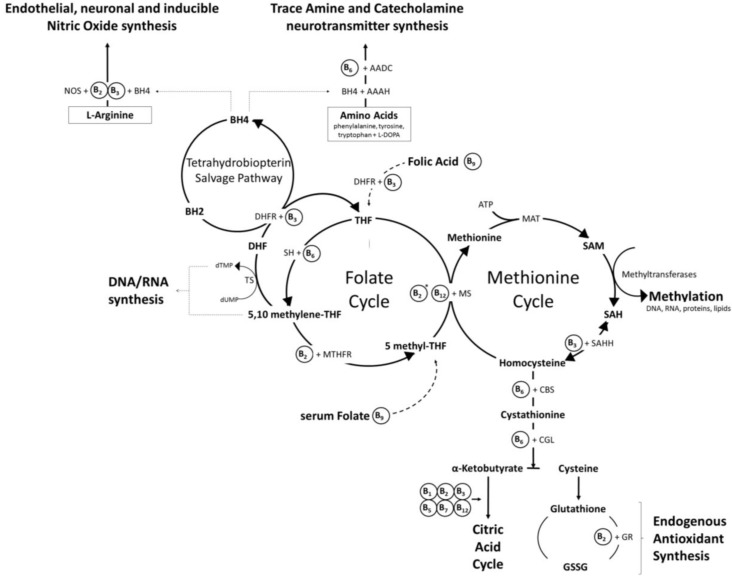
Figure 2.
The interlinked folate and methionine cycles. Dietary folate enters the folate cycle and rotates through several enzymatic modifications which generate the one-carbon units required for the synthesis of DNA/RNA and the methyl groups required to regenerate methionine from homocysteine. The “methionine cycle” provides the methyl groups required for all genomic and non-genomic methylation reactions in the form of S-adenosyl methionine (SAM). These two enzymatic cycles are essential to cellular function, including via interactions with other pathways. As an example of the latter, the re-salvaging from dihydrobiopterin of tetrahydrobiopterin, an essential cofactor in trace amine and catecholamine neurotransmitter synthesis and nitric oxide production, is rate limited by provision of the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase produced by the folate cycle. * FAD (vitamin B2) is a cofactor for methionine synthase reductase in the recycling of the vitamin B12 cofactor for methionine synthase. Abbreviations: AADC, aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase; AAAH, aromatic amino acid hydroxylases; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; BH2, dihydrobiopterin; BH4, tetrahydrobiopterin; CBS, cystathionine beta synthase; CGL, cystathionine gamma-lyase; DHFR, dihydrofolate reductase; dTMP, thymidine monophosphate; dUMP, deoxyuridine monophosphate; GR, glutathione reductase; GSSG, glutathione disulphide; MAT, methionine adenosyltransferase; MS, methionine synthase; MTHFR, methyltetrahydrofolate reductase; NOS, nitric oxide synthase; SAH, S-adenosylhomocysteine; SAHH, S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase; SAM, S-adenosyl methionine; SH, serine hydroxymethyltransferase; THF, tetrahydrofolate; TS, thymidylate synthase.