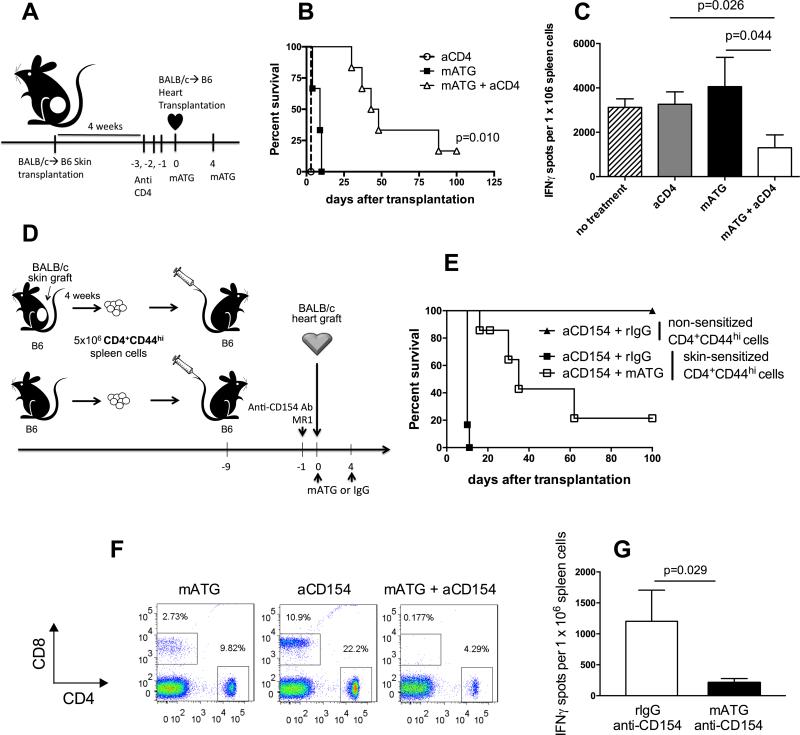
Figure 8. Inhibition of CD4 T cell help improves the efficacy of mATG induction therapy in sensitized allograft recipients.
A. B6 mice were sensitized with BALB/c skin allografts four weeks prior to BALB/c heart allograft transplantation. Sensitized heart allograft recipients were treated either with mATG alone, anti-CD4 mAb alone or mATG + anti-CD4 mAb. B. Heart allograft survival, N = 3-6 mice/group. C. Recipients anti-donor T cell responses analyzed by IFNγ ELISPOT assay at the time of rejection. Responder spleen cells were stimulated with donor BALB/c or third party SJL stimulator cells. The results are presented as mean ±SD for 3-5 mice per group. D. B6 mice were injected with 5 × 106 CD4+CD44hi cells isolated either from BALB/c skin-sensitized or naïve B6 mice followed by BALB/c heart allograft transplantation. Treatment groups included mATG alone (1 mg i.p. on days 0 and 4) or mATG + anti-CD154 mAb (clone MR1, 1 mg i.v. on day −1). E. Heart allograft survival, N = 4-6 mice per group. F. The percentages of CD8+ and CD4+ T cells among total live splenocytes at day 10 after transplantation. Flow cytometry plots are representative of 4-6 mice analyzed per group. G. Anti-donor spleen T cells responses measured by IFNγ ELISPOT assay at the time of rejection. Data are presented as mean ±SD for 4 mice per group.