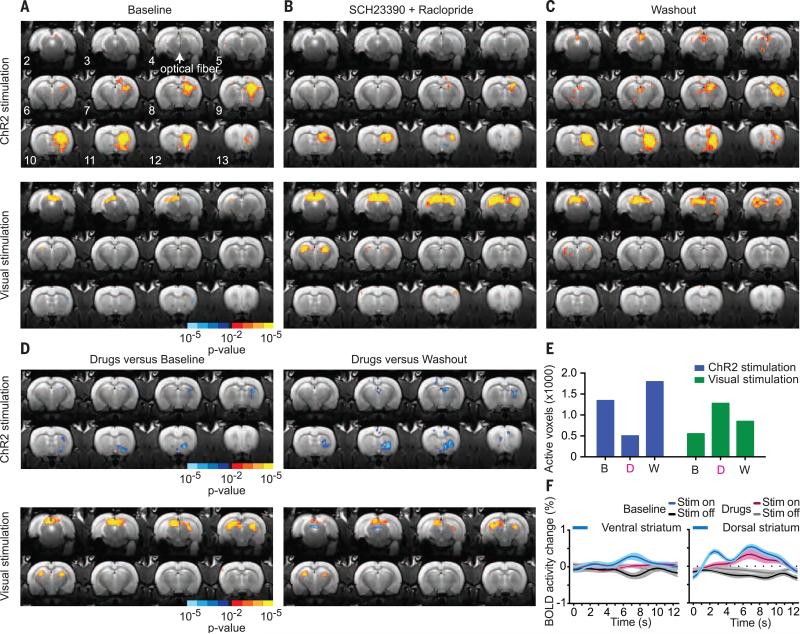
Fig. 3. Sensitivity of brainwide ofMRI BOLD patterns to dopamine receptor pharmacological inhibition.
(A to C) Sequential pharmacological experiments in ChR2-expressing TH-cre rats undergoing ChR2 stimulation of midbrain dopamine neurons (top) and visual stimulation (bottom). (A) Baseline scan (no drugs or vehicle administered, n = 4 rats, 16 runs). (B) Drug scan: systemic (intraperitoneal) administration of D1 (SCH23390, 0.6 mg/kg) and D2 (raclopride, 0.3 mg/kg) dopamine receptor antagonists immediately before acquisition of functional scans (n = 4 rats, 22 runs). (C) Vehicle control washout scan: 48 to 24 hours after drug administration (n = 4 rats, 18 runs). (D) Statistical comparison between drug-versus-baseline and drug-versus-washout conditions for ChR2 and visual stimulation. (E) Total number of activated voxels in response to ChR2 and visual stimulation under each pharmacological condition. B, baseline; D, drug; W, washout. (F) Average stimulation-locked BOLD activity time courses in the ventral and dorsal striatum in response to ChR2 stimulation of midbrain dopamine neurons at baseline (n = 4 rats, 16 runs) in the presence of systemic D1 and D2 receptor antagonists (n = 4 rats, 22 runs). Mean and SEM (n = number of runs) are shown.