Fig. 1. Mechanical allodynia after nerve injury is reversed by microglial inhibition in male but not female mice.
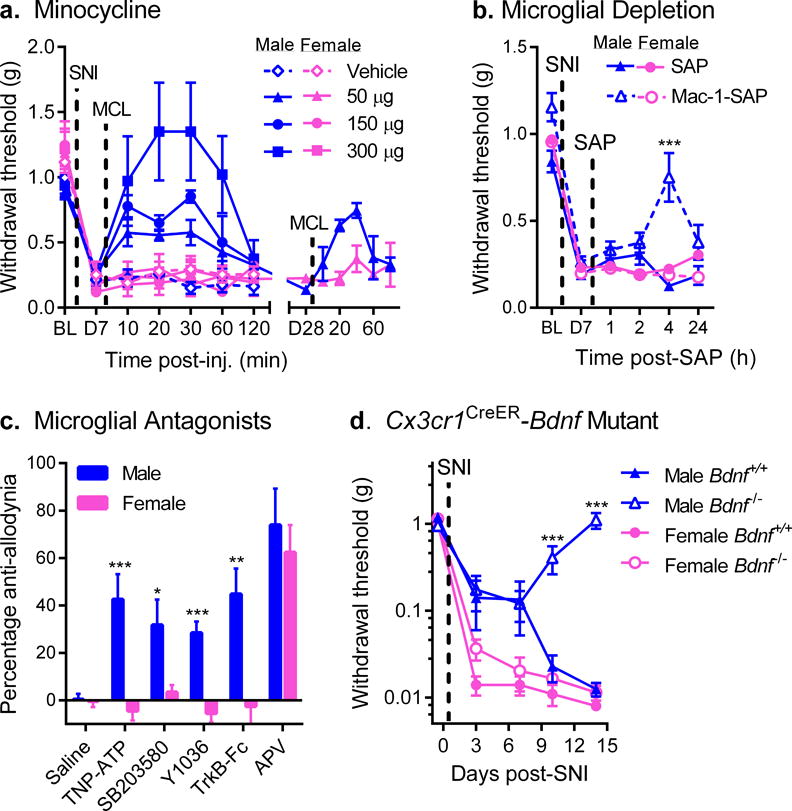
a) Reversal of established SNI-induced mechanical allodynia by intrathecal minocycline (MCL) in male but not female mice (see also Supplementary Fig. 1a). Symbols represent mean ± SEM 50% withdrawal threshold from von Frey filaments before surgery (BL), 7 days after surgery (pre-injection; D7), and 10–120 min post-injection of minocycline (n=4–5 mice/dose/sex). A different set of mice (n=4 mice/sex) were tested similarly, 28 days post-SNI (D28; right side). b) Male but not female mice treated with Mac-1-SAP display significantly reduced SNI allodynia at 4 h post-treatment. Symbols represent mean ± SEM 50% withdrawal threshold from von Frey filaments before surgery (BL), 7 days after surgery, pre-injection (D7), and 1, 2, 4 and 24 h post-SAP (n=11 mice/sex/condition). c) Intrathecal administration of the P2X inhibitor, TNP-ATP, the p38 MAPK inhibitor, SB203580, the NGF/BDNF inhibitor, Y1036, or the BDNF-sequestering fusion protein, TrkB-Fc, all block SNI-induced allodynia in male but not female mice. The NMDA receptor antagonist, APV, blocks allodynia equally in both sexes. Bars represent mean ± SEM percentage of maximal anti-allodynia (see Methods; n=8 mice/sex/drug). d) Development of SNI-induced mechanical allodynia in male and female mice lacking central nervous system microglial BDNF (i.e., with tamoxifen-induced Cre-loxP-mediated deletion of the Bdnf gene in CX3CR1-positive cells). Mutant (Bdnf−/−) male mice fail to develop full allodynia displayed by female Bdnf−/− and wildtype (Bdnf+/+) mice. Symbols represent mean ± SEM absolute withdrawal threshold from von Frey filaments before and 3, 7, 10 and 14 days post-surgery (n=4–8 mice/sex/genotype). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 compared to corresponding female mice by t-test.
