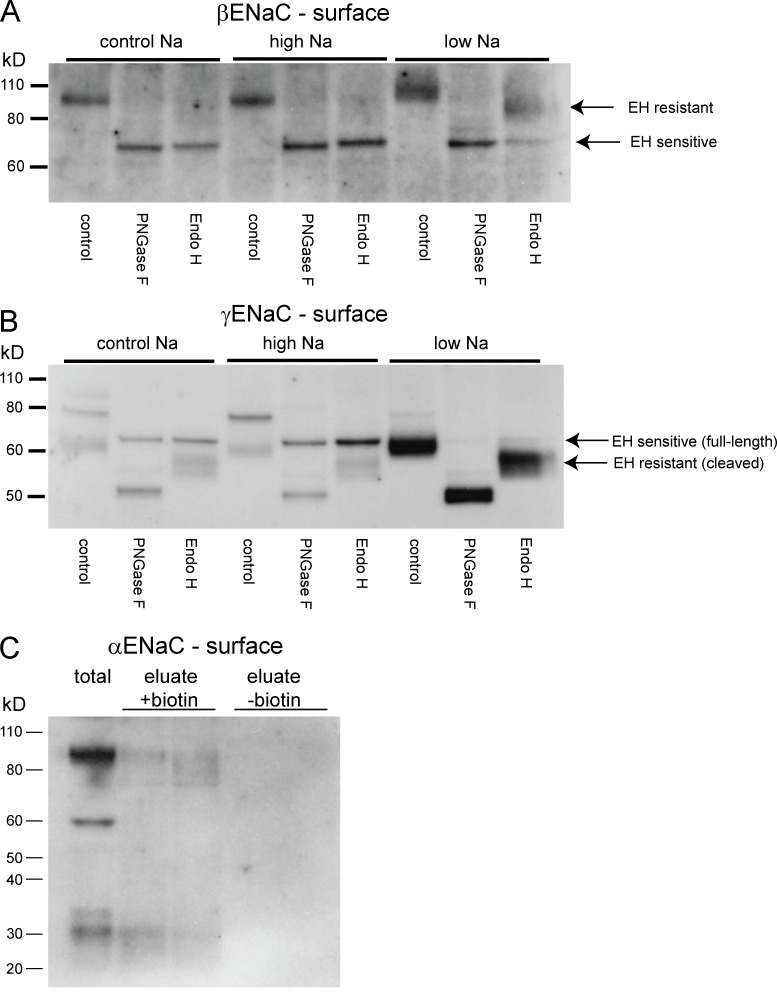
Figure 1.
Expression of EndoH-sensitive and -resistant forms of ENaC at the cell surface. (A and B) Surface membrane fractions were isolated from biotinylated kidneys. These fractions were treated with either EndoH (to cleave high-mannose N-linked glycosylation trees) or PNGaseF (to cleave all trees). These products were separated using SDS-PAGE and probed with antibodies against the C terminus of βENaC (A) or γENaC (B). In both cases, EndoH (EH)-sensitive and -resistant forms were observed. EndoH-resistant subunits were much more abundant when animals were fed a low-Na diet. (C) Biotinylated fractions were probed with antibodies against the N termini of αENaC. Both full-length (∼90 kD) and cleaved (∼30 kD) forms of the subunit were detected, in addition to protein with a diffuse molecular mass of 75–90 kD. Eluates from nonbiotinylated kidney extracts did not have detectable signals.