Figure 10. Proposed model by which HCV infection induces NFĸB and TGF-β1 through ER stress and the UPR pathway in a JNK-dependent manner.
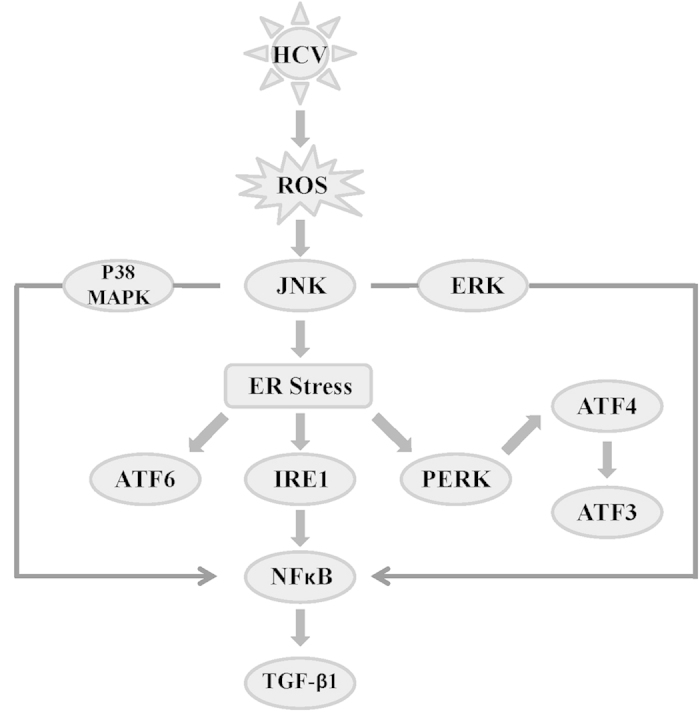
HCV induces ROS induction, which in turn activates the phosphorylation of JNK. The phosphorylated JNK subsequently induces ER stress. The activation of one arm of UPR pathway, IRE1, induces the phosphorylation of NFκB. The activated NFκB is translocated to nucleus and up-regulates TGF-β1 expression.
