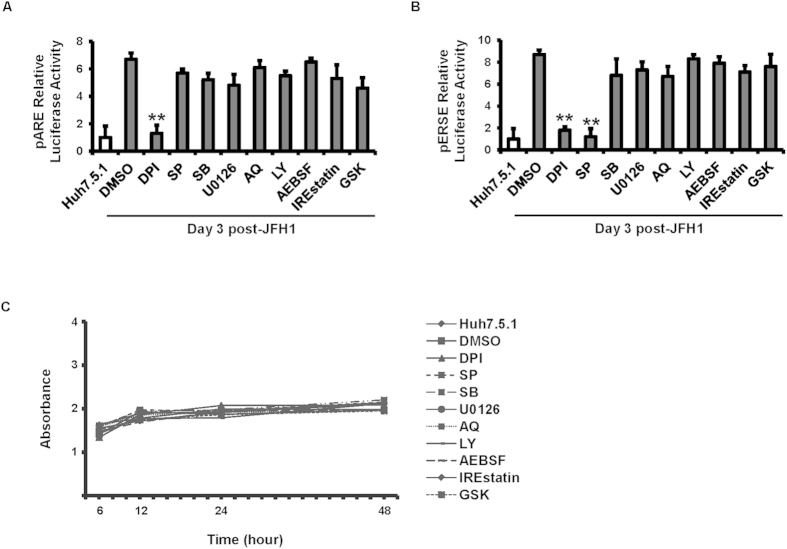
Figure 3. ROS and JNK inhibition decreased HCV-induced ER stress and UPR activation.
Huh7.5.1 cells and Huh7.5.1 infected with JFH1 for 3 days were transfected with plasmid pARE or pERSE-luciferase reporter. The pRL-TK expression Renilla luciferase was co-transfected as an internal control. After 24 hours of transfection, cells were treated with several pathway inhibitor including DPI, SB, SP, U0126, LY, AEBSF, IREstatin, and GSK at 20 μM each. 1% DMSO was used as a negative control. ARE-mediated Nrf2 and ER stress signaling pathway were monitored by dual luciferase reporter assay at 24 hours after inhibitor treatment. Relative luciferase activity (RLA) was normalized by dividing the firefly luciferase value by the Renilla luciferase value. DPI (ROS inhibitor) decreased HCV-induced ARE signaling in JFH1-infected Huh7.5.1 cells. DPI and SP (JNK inhibitor) blocked HCV-induced ERSE signaling in JFH1-infected cells (Fig. 3A,B). There was no significant difference in proliferation between untreated and inhibitor treated cells at 6, 12, 24, and 48 hours of the treatment (Fig. 3C). **p < 0.01 for comparison of indicated treatment to the JFH1-infected cells in DMSO.