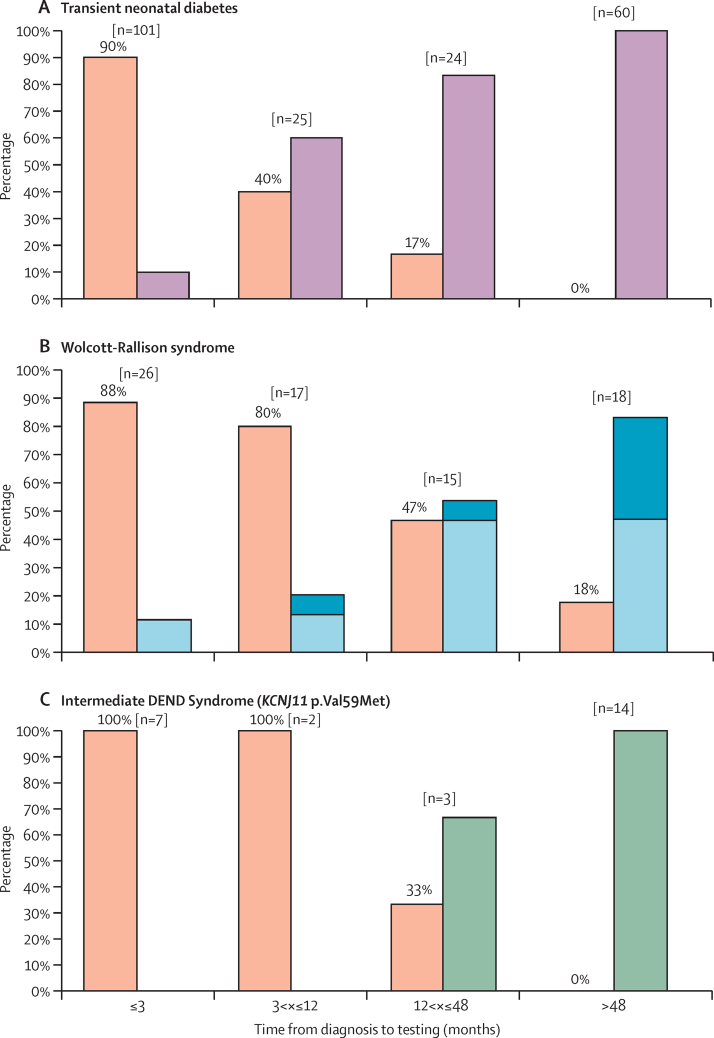
Figure 4.
Genetic diagnosis precedes development of additional clinical features defining the neonatal diabetes subtype
(A) Effect of early genetic diagnosis in transient neonatal diabetes caused by 6q24 methylation defects or potassium channel gene mutations. Bar chart representing clinical features at the time of genetic testing for neonatal diabetes. Orange=diabetes, purple=diabetes remitted. (B) The effect of age at genetic testing on whether patients have non-diabetes features of Wolcott-Rallison Syndrome at the time of referral for genetic testing. Bar chart representing clinical features at the time of genetic testing for neonatal diabetes. Orange=diabetes only, light blue=diabetes and either skeletal abnormalities or liver dysfunction, dark blue=diabetes, skeletal abnormalities, and liver dysfunction. (C) The effect of age at genetic testing on whether patients with a KCNJ11 p.Val59Met mutation have neurological features at the time of referral for genetic testing. Bar chart representing clinical features at the time of genetic testing for neonatal diabetes. Orange=diabetes only, green=diabetes and neurological features.