ABSTRACT
The presence of the Lon protease in all three domains of life hints at its biological importance. The prokaryotic Lon protease is responsible not only for degrading abnormal proteins but also for carrying out the proteolytic regulation of specific protein targets. Posttranslational regulation by Lon is known to affect a variety of physiological traits in many bacteria, including biofilm formation, motility, and virulence. Here, we identify the regulatory roles of LonA in the human pathogen Vibrio cholerae. We determined that the absence of LonA adversely affects biofilm formation, increases swimming motility, and influences intracellular levels of cyclic diguanylate. Whole-genome expression analysis revealed that the message abundance of genes involved in biofilm formation was decreased but that the message abundances of those involved in virulence and the type VI secretion system were increased in a lonA mutant compared to the wild type. We further demonstrated that a lonA mutant displays an increase in type VI secretion system activity and is markedly defective in colonization of the infant mouse. These findings suggest that LonA plays a critical role in the environmental survival and virulence of V. cholerae.
IMPORTANCE Bacteria utilize intracellular proteases to degrade damaged proteins and adapt to changing environments. The Lon protease has been shown to be important for environmental adaptation and plays a crucial role in regulating the motility, biofilm formation, and virulence of numerous plant and animal pathogens. We find that LonA of the human pathogen V. cholerae is in line with this trend, as the deletion of LonA leads to hypermotility and defects in both biofilm formation and colonization of the infant mouse. In addition, we show that LonA regulates levels of cyclic diguanylate and the type VI secretion system. Our observations add to the known regulatory repertoire of the Lon protease and the current understanding of V. cholerae physiology.
INTRODUCTION
Vibrio cholerae is a facultative human pathogen that inhabits aquatic ecosystems around the world. This Gram-negative bacterium survives and persists in aquatic environments by living in aggregates enclosed by a self-produced matrix of exopolysaccharides, proteins, and nucleic acids, known as biofilms (1). It has been shown that growth in the biofilm state confers a range of benefits to V. cholerae, including resistances to protozoan predation, bacteriophage infection, and nutrient limitation and increases in the colonizing and virulence capabilities of the bacterium (2–4). The main components of V. cholerae biofilms are Vibrio polysaccharide (VPS) and the matrix proteins RbmA, RbmC, and Bap1 (5–9). The transcription of the genes that code for these matrix components and their biosynthetic enzymes is primarily controlled by the transcriptional regulatory proteins VpsR, VpsT, and HapR (10–12). VpsR and VpsT bind directly to the upstream regulatory regions of the vps-I and vps-II operons and directly activate the expression of vps genes (13). Quorum sensing (QS) acts to repress biofilm formation in V. cholerae at high cell densities by activating the production of HapR, which then directly affects the transcription of vps structural genes and vpsT (12, 13).
Regulatory circuits that control biofilm formation in V. cholerae are influenced by cellular levels of cyclic diguanylate (c-di-GMP) (14). An increase in intracellular c-di-GMP levels has been shown to positively regulate biofilm formation, while motility is decreased (15). The enzymes that synthesize c-di-GMP from two molecules of GTP are known as diguanylate cyclases (DGCs) and contain a GGDEF motif (16). The enzymes that degrade c-di-GMP into either pGpG or two molecules of GMP are known as phosphodiesterases (PDEs) and contain an EAL or HD-GYP motif, respectively (16). Collectively, the activities of these DGCs and PDEs control the amount of c-di-GMP in the cell in response to various environmental signals (16).
V. cholerae is the causative agent of the life-threatening infection known as cholera, which occurs when the bacterium colonizes the small intestine and produces the major virulence factors toxin-coregulated pili (TCP) and cholera toxin (CT), thereby inducing severe diarrhea (17). The regulation of CT and TCP is controlled by multiple regulatory circuits. The transcriptional regulator HapR, a protein whose production is determined by the various quorum-sensing pathways of V. cholerae, is one of the critical regulators of virulence (18). Under conditions of low cell density, HapR production is inhibited, and its repressive activity on the expression of the transcriptional regulator AphA is relieved. AphA, along with AphB, activates the production of TcpPH, and AphA and AphB then act in concert with ToxRS to activate the transcription of toxT (19). The production of CT and TCP is then directly activated by ToxT (20).
The type VI secretion system (T6SS) also contributes to virulence in V. cholerae and can provide protection and a competitive advantage in interactions with environmental competitors and predators (21, 22). The T6SS apparatus resembles a tube within a tube, in which the outer tube is a phage-like contractile sheath and the inner tube is made up of multiple units of hemolysin-coregulated protein (Hcp). The outer tube is believed to provide the mechanical force necessary to inject effector proteins into adjacent prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells in response to cell-to-cell contact in order to kill or inhibit the target cell (23, 24). The genes coding for the T6SS apparatus are located in one main cluster (VCA0105 to VCA0124) and two auxiliary clusters (VCA0017 to VCA0022 and VC1415 to VC1421) (21, 25). The genes of the T6SS are negatively regulated by the global regulator TsrA, the quorum-sensing (QS) regulator LuxO, and the osmolarity-responsive transcriptional regulator OscR, and they are positively regulated by HapR, cyclic AMP receptor protein (CRP), response regulator VxrB, and VasH (26–30).
While the transcriptional regulation and posttranscriptional regulation of motility, biofilm formation, and cellular levels of c-di-GMP have been studied intensely, we are just beginning to understand what effects posttranslational proteolytic regulation has on these processes (31–35). Recent studies documented that regulatory proteolysis in V. cholerae impacts virulence through modulation of the transcriptional regulators TcpP by YaeL (RseP) and Tsp proteases and ToxR by the RseP protease (36–38). Another protease that might play a significant role in V. cholerae physiology that has been linked to motility, biofilm formation, and virulence in a variety of other bacterial species is the Lon protease. This protease is composed of six identical subunits that form a hexameric ring structure characteristic of AAA+ ATPase domains (39, 40). The LonA protein, encoded by V. cholerae VC1920, shares 82% identity with its Escherichia coli homolog. In E. coli, the Lon protease has been shown to be responsible for ∼50% of the damaged protein turnover and the regulation of various processes, such as the SOS response and capsular polysaccharide synthesis (41). In a variety of bacterial species, including Gram-negative and Gram-positive organisms, Lon has been shown to be involved in the regulation of motility and virulence in relation to a range of host organisms and infection models (40).
In this work, we investigated the role that LonA plays in several behaviors central to the lifestyle of V. cholerae. We show that LonA contributes to the biofilm formation, motility, and virulence of V. cholerae. For the first time, we also show that levels of intracellular c-di-GMP and the expression of the T6SS are influenced by LonA.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Ethics statement.
All animal procedures used were in strict accordance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (42) and were approved by the University of California (UC), Santa Cruz, Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee, Santa Cruz, CA (approval number Yildf1206).
Strains and growth conditions.
The strains used in this study are listed in Table S1 in the supplemental material. V. cholerae and E. coli strains were grown aerobically in Luria-Bertani (LB) broth (1% tryptone, 0.5% yeast extract, 1% NaCl [pH 7.5]) at 30°C and 37°C, respectively. LB agar contained granulated agar (Difco) at 1.5% (wt/vol). Medium additives were used when necessary at the following concentrations: rifampin, 100 μg/μl; ampicillin, 100 μg/μl; and chloramphenicol, 20 μg/μl for E. coli and 5 μg/μl or 2.5 μg/μl for V. cholerae.
Strain and plasmid construction.
Plasmids were constructed using standard cloning methods or the Gibson Assembly recombinant DNA technique (New England BioLabs, Ipswich, MA). Gene deletions were carried out using allele exchange of the native open reading frame (ORF) with the truncated ORF, as previously described (43). The complementation of lonA was carried out using a Tn7-based system that inserted the ORF of lonA accompanied by 178 bp of upstream genomic sequence into the conserved Tn7 site at the 3′ end of the glmS gene, as previously described (28). Transcriptional fusions were constructed by cloning the upstream regulatory regions of selected genes into the pBBRlux plasmid, as previously described (13). The exact lengths of the upstream regulatory region used for the construction of these fusions are listed in Table S1 in the supplemental material.
Biofilm assays.
Biofilm formation assays in flow cell chambers were carried out as previously described, with slight modifications (44). To image the biofilms, the flow was stopped, tubing was disconnected, and each chamber was washed three times with 200 μl of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). The biofilms were then stained in the chambers with a 1.3 μM solution of nucleic acid staining dye Syto9 (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA) in 1× PBS for 30 min. After being incubated with the stain, the chambers were washed three times with 200 μl of PBS and promptly imaged using confocal laser-scanning microscopy (LSM) (5-Pa LSM; Zeiss). The resulting image z-stacks were analyzed using Imaris (Bitplane, Concord, MA) and COMSTAT (45). Three independent biological replicates were each imaged three times for every time point. Statistical analysis of the COMSTAT results was carried out using an analysis of variance (ANOVA). Dunnett's multiple-comparison test identified samples that differed significantly from the biofilms formed by the wild-type strain.
Tube biofilms were grown in silicone tubing with an internal diameter of 0.125 in. under constant-flow conditions for the purpose of quantifying c-di-GMP and acquiring luminescence reporter readings from biofilm cells. To inoculate the tubing, overnight cultures of V. cholerae wild-type and ΔlonA mutant strains were diluted in LB broth to an optical density at 600 nm (OD600) of 0.15, and 10-ml Luer-Lok syringes were used to deliver these dilutions to the entire length of silicone tubing. Cells were then allowed to attach to the surface of the tubing for 1 h before flow was started. A peristaltic pump was used to deliver constant flow at a rate of 4.4 ml per h. Full-strength LB broth was used to ensure sufficient growth. Biofilms were allowed to develop for 24 h at 25°C. To harvest the biofilms, the tubing was detached from flow, drained of excess medium and loosely adhering cells, and scraped from the tubing.
Motility assays.
Soft agar motility plates were made using LB medium with 0.3% (wt/vol) agar. The plates were inoculated by briefly stabbing the agar from an overnight colony of the strains to be tested. The plates were then incubated at 30°C for 5 to 6 h until the diameters of the migration zones were measured. To compare the motility of different strains, two-tailed Student's t tests were used.
Determination of intracellular c-di-GMP levels.
c-di-GMP extraction was performed as described previously (43). The V. cholerae wild-type, ΔlonA mutant, and ΔlonA Tn7::lonA- complemented strains were grown in LB broth to an OD600 of 0.4 before 40 ml was collected for c-di-GMP quantification from planktonic cells. In order to quantify c-di-GMP from the biofilm cells, biofilms were grown in 60-cm sections of tubing, as described above. The biofilms were resuspended in 44 ml of 1× PBS after 24 h of growth. c-di-GMP was quantified from 40 ml of this resuspension. The amount of c-di-GMP in samples was calculated with a standard curve generated from pure c-di-GMP suspended in 184 mM NaCl (BioLog Life Science Institute, Bremen, Germany). The concentrations used for standard curve generation were 50 nM, 100 nM, 500 nM, 2 μM, 3.5 μM, 5 μM, 7.5 μM, and 10 μM. The assay is linear from 50 nM to 10 μM, with an R2 of 0.999. The c-di-GMP levels were normalized to total protein per milliliter of culture.
To determine protein concentration, 4 ml from each culture or biofilm resuspension was pelleted, the supernatant was removed, and cells were lysed in 1 ml of 2% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS). Total protein in the samples was estimated with a bicinchoninic acid (BCA) assay (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA) using bovine serum albumin (BSA) as the standard. Each c-di-GMP quantification experiment was performed with four biological replicates. Levels of c-di-GMP were compared between the samples using a two-tailed Student's t test.
Gene expression profiling.
The microarrays used were composed of spotted 70-mer oligonucleotides representing the open reading frames of the V. cholerae strain N16961 genome and were printed at the University of California, Santa Cruz, Santa Cruz, CA (46). A common reference RNA sample was used for all whole-genome expression analyses. Reference RNA was sampled from V. cholerae grown overnight at 30°C in LB broth, diluted 1:200 in fresh medium, and harvested at mid-exponential phase at an OD600 of 0.3. Experimental RNA samples were prepared by diluting overnight-grown cultures of V. cholerae 1:200 in LB and incubated at 30°C until exponential phase (OD600, 0.3). RNA was isolated as previously described (46). To remove contaminating DNA, total RNA was incubated with DNase I (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA), and the RNeasy minikit (Qiagen) was used to clean up the RNA after DNase digestion. Microarray hybridization and scanning were performed as described previously (46). Normalized signal ratios were obtained with locally weighted scatterplot smoothing (LOWESS) print-tip normalization, using the Bioconductor packages (47) in the R environment. Differentially regulated genes were determined using three biological replicates and two technical replicates for each treatment (six data points for each spot), using the Significance Analysis of Microarrays (SAM) program (48), with a 1.5-fold difference in gene expression and a 3% false-discovery rate (FDR) as cutoff values.
Luminescence assay.
Wild-type V. cholerae and the ΔlonA mutant harboring transcriptional reporters were grown aerobically overnight in LB broth supplemented with chloramphenicol. For luminescence measurements from planktonic cells, overnight cultures were diluted 1:200 in LB broth plus chloramphenicol and grown at 30°C to an OD600 of 0.3 or 1.0. For luminescence measurements from the biofilm cells, biofilms were grown in 30-cm sections of tubing, as described above, using LB broth supplemented with chloramphenicol. Biofilms were grown for 24 h before being resuspended in 15 ml of 1× PBS, and measurements were taken. Luminescence was measured using a Victor3 multilabel counter (PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA) and is reported as counts per minute per milliliter divided by the OD600. The assays were repeated, with at least three biological replicates for all strains tested. Four technical replicates were measured for all assays. Statistical analysis was performed using a two-tailed Student's t test.
Analysis of Hcp production and secretion.
V. cholerae strains were grown to an OD600 of 2.0, and the culture (25 ml) was centrifuged at 20,000 × g for 15 min to obtain whole-cell pellets. The culture supernatant containing secreted proteins was filtered through 0.22-μm-pore-size membranes (Millipore, Billerica, MA), and secreted proteins in the culture supernatant were precipitated overnight at 4°C with 13% trichloroacetic acid (TCA), pelleted by centrifugation at 47,000 × g for 30 min at 4°C, washed with ice-cold acetone, and resuspended in 1× PBS containing Complete protease inhibitor (Roche, Basel, Switzerland). Bovine serum albumin (BSA) (100 μg/ml) was added to the culture supernatant prior to TCA precipitation as a control. Protein pellets from the whole-cell protein were suspended in 2% SDS, and protein concentrations were estimated using a Pierce BCA protein assay kit (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA). Equal amounts of total protein (20 μg) or equal volumes of TCA-precipitated supernatant samples were loaded into 12% SDS polyacrylamide gels for SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). Western blotting analyses were performed, as described previously (9), using anti-Hcp polyclonal antiserum provided by the S. N. Wai lab (26), anti-RNA polymerase alpha (anti-RNAPα) (BioLegend, San Diego, CA), and anti-BSA (Santa Cruz Biotech, Santa Cruz, CA). For whole-cell Western blotting, Hcp and RNAPα were probed for on separate yet identical blots. For Western blots using supernatant samples, Hcp, RNAPα, and BSA were probed for in succession on the same blot. These experiments were conducted with at least three biological replicates.
Bacterial killing assay.
Killing assays were performed as described previously (28). Briefly, bacterial strains were grown overnight on LB plates containing 340 mM NaCl, and single colonies were used to inoculate LB broth containing 340 mM NaCl. Overnight cultures of V. cholerae and E. coli MC4100 were mixed at a 10:1 ratio, and 25 μl was spotted onto 0.22-μm-pore-size-filter cellulose ester membranes (Merck Millipore, Billerica, MA) lying on LB agar plates containing 340 mM NaCl and incubated at 37°C for 4 h. E. coli diluted 1:10 in LB broth was plated and incubated under the same conditions as described above for comparison. All spots were harvested, serially diluted in PBS, and plated onto LB plates containing 50 μg/ml streptomycin to enumerate the surviving E. coli prey cells.
Intestinal colonization assay.
An in vivo competition assay for intestinal colonization was performed as described previously (49). A V. cholerae lonA mutant strain (lacZ+) and the fully virulent otherwise-wild-type strain (lacZ mutant) were grown to stationary phase at 30°C with aeration in LB broth. The ΔlonA mutant and wild-type strain were mixed to approach a 1:1 CFU ratio in PBS. The inoculum was plated on LB agar plates containing 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indoyl-β-d-galactopyranoside (X-Gal) to differentiate wild-type and mutant colonies and to determine the input ratio. Approximately 105 CFU was intragastrically administered to groups of seven anesthetized 5-day-old CD-1 mice (Charles River Laboratories, Hollister, CA). After 20 h of incubation, the small intestine was removed, weighed, homogenized, and plated on appropriate selective and differential media to enumerate mutant and wild-type cells recovered and to obtain the output ratios. In vivo competitive indices were calculated by dividing the small intestine output ratio of the mutant to wild-type strains by the inoculum input ratio of the mutant to wild-type strains. Statistical analyses were performed using the Prism 5 software (GraphPad Software, Inc., San Diego, CA) using a Wilcoxon signed-rank test. P values of <0.05 were determined to be statistically significant.
Microarray data accession number.
The microarray data have been deposited in the National Center for Biotechnology Information Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database (accession no. GSE73023).
RESULTS
LonA contributes to biofilm formation in V. cholerae.
To assess what effects LonA might have on V. cholerae physiology, a strain lacking lonA in the wild-type genetic background and a complementation strain harboring a single copy of lonA at the target site of the Tn7 transposon in the ΔlonA mutant genetic background were created.
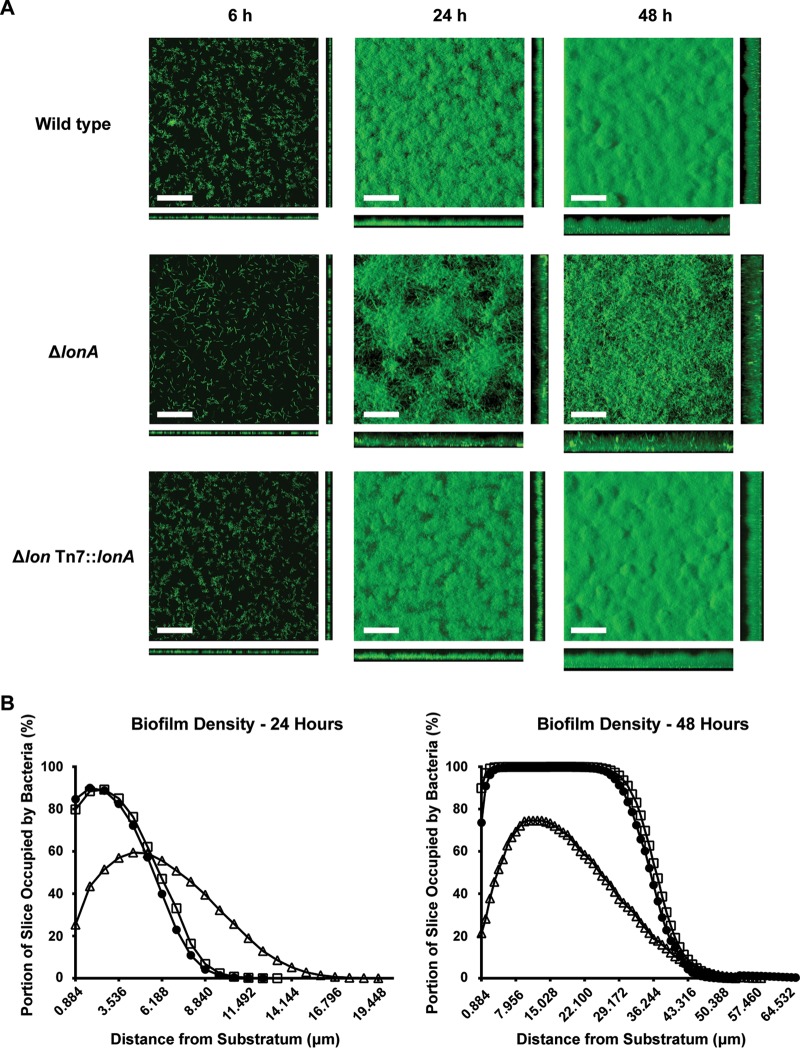
Biofilm formation was analyzed for the ΔlonA mutant, lonA-complemented, and wild-type strains by growing them in flow cells. Biofilms were grown under flow conditions, stained with Syto9, and imaged using confocal laser-scanning microscopy at 6, 24, and 48 h postinoculation. At 6 h postinoculation, the wild-type and lonA-complemented strains had begun to form compact clusters of cells, known as microcolonies, while the ΔlonA mutant biofilm was composed of single cells that showed no obvious signs of cell-to-cell adhesion (Fig. 1A). Quantitative analysis of the biofilm images was made possible by the program COMSTAT, which was designed specifically for the quantification of three-dimensional biofilm images (45). COMSTAT allowed us to analyze the biomass, average and maximum thicknesses, substratum coverage, and roughness of each biofilm image stack. Quantitative analysis by COMSTAT revealed that the 6-h ΔlonA mutant biofilm had significantly less biomass and less average thickness than those of the 6-h wild-type and complemented-strain biofilms (Table 1). Differences in the biofilms formed by the ΔlonA mutant became apparent at 24 h. While the wild-type and complemented strains had formed compact mats of cells with uniform pillars and crevices characteristic of a mature V. cholerae biofilm, the ΔlonA mutant had grown into a porous web-like formation of filamentous cells with large gaps in the biomass, in which the substratum was still visible (Fig. 1A). These ΔlonA mutant biofilms did not have a significant decrease in overall biomass compared to that of the wild-type and complemented strains, while the thickness of the biofilms was visibly greater for the ΔlonA mutant (Fig. 1A). The COMSTAT analysis corroborated this observation by revealing that the maximum thickness of the biofilm is nearly doubled for the ΔlonA mutant compared to that of the wild type, with mean ± standard deviation heights of 20.04 ± 1.40 μm and 10.71 ± 1.28 μm, respectively (Table 1). The trends in biomass and maximum thickness revealed by COMSTAT in the 24-h biofilms did not reappear at 48 h. The biomass of the ΔlonA mutant biofilms had significantly decreased compared to that of both the wild-type and complemented strains, while the average and maximum heights of all three strains had become roughly equal (Fig. 1 and Table 1). Substratum coverage at all three time points was visually and quantitatively decreased in the ΔlonA mutant biofilms compared to that of the wild-type or complemented biofilms (Table 1).
FIG 1.
Biofilm formation of the ΔlonA and complemented strains. (A) Top-down and orthogonal views of biofilms formed by wild-type, ΔlonA, and lonA-complemented strains after 6, 24, and 48 h. Scale bars = 40 μm. Biofilms were grown in flow cells and stained with Syto9 prior to being imaged. (B) Biofilm density was determined using COMSTAT analysis of 24- and 48-h biofilms. The results shown are from one representative biofilm of three biological replicates. Circles, wild type; triangles, ΔlonA mutant; squares, lonA Tn7::lonA strain.
TABLE 1.
COMSTAT analysis of biofilms formed after 6, 24, and 48 h by the wild-type, Δlon, and Δlon Tn7::lon strainsa
| Time postinoculation and strain | Biomass (μm3/μm2) | Mean thickness (SD) (μm) |
Substrate coverageb | Roughness coefficient | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avg | Maximum | ||||
| 6 h | |||||
| Wild type | 0.34 (0.06) | 0.21 (0.07) | 4.71 (1.10) | 0.15 (0.11) | 1.71 (0.05) |
| Δlon mutant | 0.16 (0.03)*** | 0.11 (0.02)** | 4.32 (0.70)NS | 0.06 (0.01)*** | 1.87 (0.02)*** |
| Δlon Tn7::lon strain | 0.35 (0.04)NS | 0.22 (0.04)NS | 5.30 (0.44)NS | 0.14 (0.02)NS | 1.71 (0.03)NS |
| 24 h | |||||
| Wild type | 4.08 (1.03) | 3.69 (0.88) | 10.71 (1.28) | 0.69 (0.15) | 0.47 (0.14) |
| Δlon mutant | 3.81 (1.55)NS | 5.09 (1.43)* | 20.04 (1.40)*** | 0.19 (0.11)*** | 0.69 (0.20)* |
| Δlon Tn7::lon strain | 5.25 (0.56)NS | 4.67 (0.57)NS | 13.47 (1.06)** | 0.75 (0.07)NS | 0.36 (0.05)NS |
| 48 h | |||||
| Wild type | 31.81 (3.17) | 32.40 (2.43) | 52.16 (5.27) | 0.70 (0.11) | 0.12 (0.02) |
| Δlon mutant | 20.02 (2.54)*** | 31.94 (2.15)NS | 56.77 (2.72)* | 0.21 (0.06)*** | 0.22 (0.03)*** |
| Δlon Tn7::lon strain | 35.15 (1.62)* | 34.88 (1.50)* | 50.49 (2.98)NS | 0.89 (0.09)** | 0.10 (0.01)NS |
The total biomass, average and maximum thicknesses, substrate coverage, and roughness coefficient were calculated using COMSTAT. The values presented are the means and standard deviations of data from at least nine z-series image stacks. Significance was determined by an ANOVA. Dunnett's multiple-comparison test identified samples whose values differ significantly from those of biofilms formed by the wild-type strain. NS, differences were not significant, *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.001; ***, P ≤ 0.0001.
A value of 0 indicates no coverage (equivalent to 0%), while a value of 1 indicates full coverage (equivalent to 100%).
Due to the change in the ΔlonA mutant's biofilm thickness and substratum coverage, with no change in biomass at 24 h, we wondered if we could better analyze the compactness of the biofilms. By using COMSTAT to determine how much of each slice of each image z-stack was occupied by bacteria from the substratum to the top of the biofilm, we constructed a graph representing the cellular density of the biofilms (Fig. 1B). This was done for both 24- and 48-h biofilms in order to assess what structural changes might be taking place between the wild-type and ΔlonA mutant biofilms between these time points (Fig. 1B). The 24-h-biofilm density graphs made it clear that the ΔlonA mutant formed biofilms that had maximum cell density further away from the substratum than the wild-type strain while also growing to an increased height, effectively creating a more porous biofilm with decreased density in respect to biomass (Fig. 1B). The 48-h-biofilm density graph revealed that while the ΔlonA mutant biofilms had increased in height and biomass compared to the 24-h biofilms, they were never able to achieve >80% slice coverage at any distance from the substratum. Wild-type biofilms achieved close to 100% slice coverage from 0 to 30 μm from the substratum, revealing a significant difference in biofilm density between the ΔlonA mutant and wild type. Overall, these results suggest that the ability of a V. cholerae ΔlonA mutant to produce a biofilm is significantly altered.
LonA affects motility in V. cholerae.
After seeing major differences in biofilm formation in the absence of LonA, and considering that this process is inversely regulated with motility in V. cholerae, we wanted to know if motility was also affected by this intracellular protease. We measured swimming motility in the ΔlonA mutant by performing a motility assay on soft agar plates. When grown for 5.5 h at 30°C, the average migration zone diameter of the ΔlonA mutant was 5.2 cm, while both the wild-type and complemented strains had diameters of 3.1 cm (Fig. 2). Therefore, V. cholerae motility nearly doubles in the absence of LonA and returns to wild-type levels with the introduction of the lonA gene.
FIG 2.
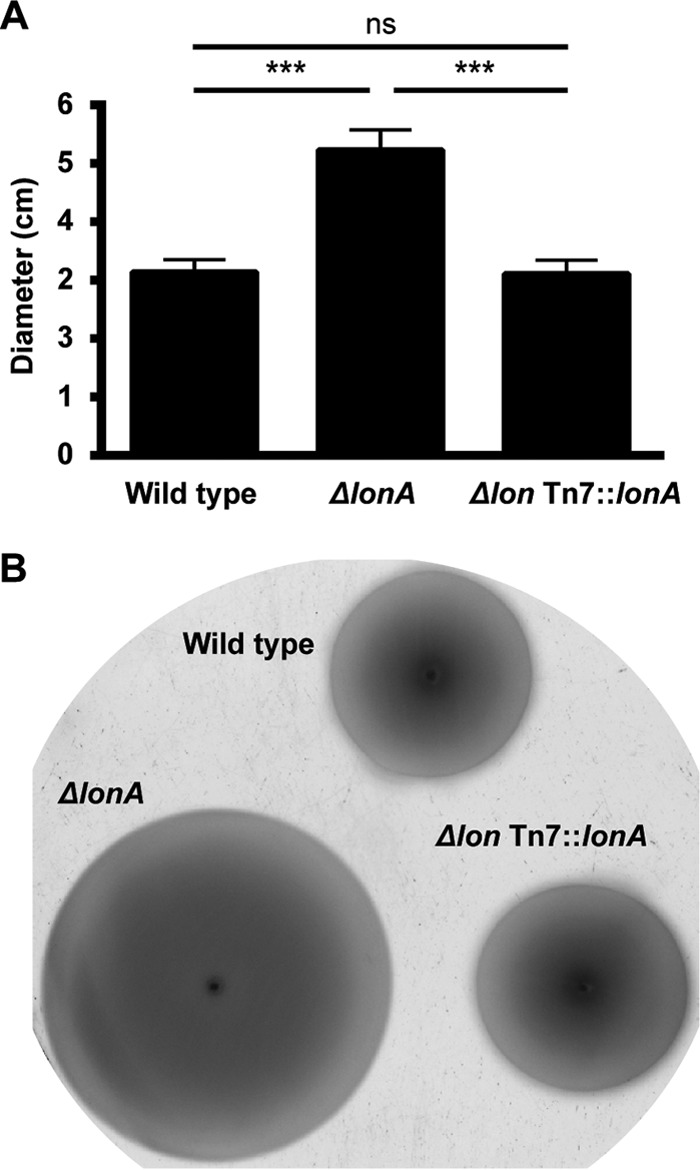
Swimming motility of the ΔlonA and complemented strains. (A) The wild-type, ΔlonA, and lonA-complemented strains were grown on LB agar plates containing 0.3% agar at 30°C for 5.5 h before migration zones were measured. The error bars indicate the standard deviations of the results from 9 biological replicates. ***, P ≤ 0.0001 by Student's t test; ns, differences were not significant. (B) Migration zones of wild-type, ΔlonA, and lonA-complemented strains after 5.5 h of growth on 0.3% agar plates.
Levels of intracellular c-di-GMP are altered in planktonic and biofilm cells of a ΔlonA mutant.
The hypermotile and abnormal biofilm formation phenotypes of a ΔlonA mutant prompted us to evaluate c-di-GMP levels. To determine if levels of c-di-GMP were being affected in the ΔlonA strain, we extracted and quantified c-di-GMP from planktonic cells of the wild-type, ΔlonA mutant, and lonA-complemented strains. The quantification of c-di-GMP revealed that exponentially growing planktonic ΔlonA mutant cells had a small but significant decrease in intracellular c-di-GMP levels compared to those of the wild type (Fig. 3A). We also quantified intracellular c-di-GMP in the biofilms of wild-type and ΔlonA strains to assess whether LonA affects the characteristic increase in intracellular c-di-GMP found in biofilm cells. Biofilms were allowed to grow in silicone tubing for 24 h under constant flow before being collected for c-di-GMP quantification. As expected, wild-type biofilm cells had more c-di-GMP than their planktonic counterparts (Fig. 3). In contrast to planktonic cells, biofilms of the ΔlonA strain had a significant increase in c-di-GMP levels compared to those of the wild type (Fig. 3B). These results suggests that LonA plays a role in regulating levels of c-di-GMP in both planktonic and biofilm cells of V. cholerae.
FIG 3.
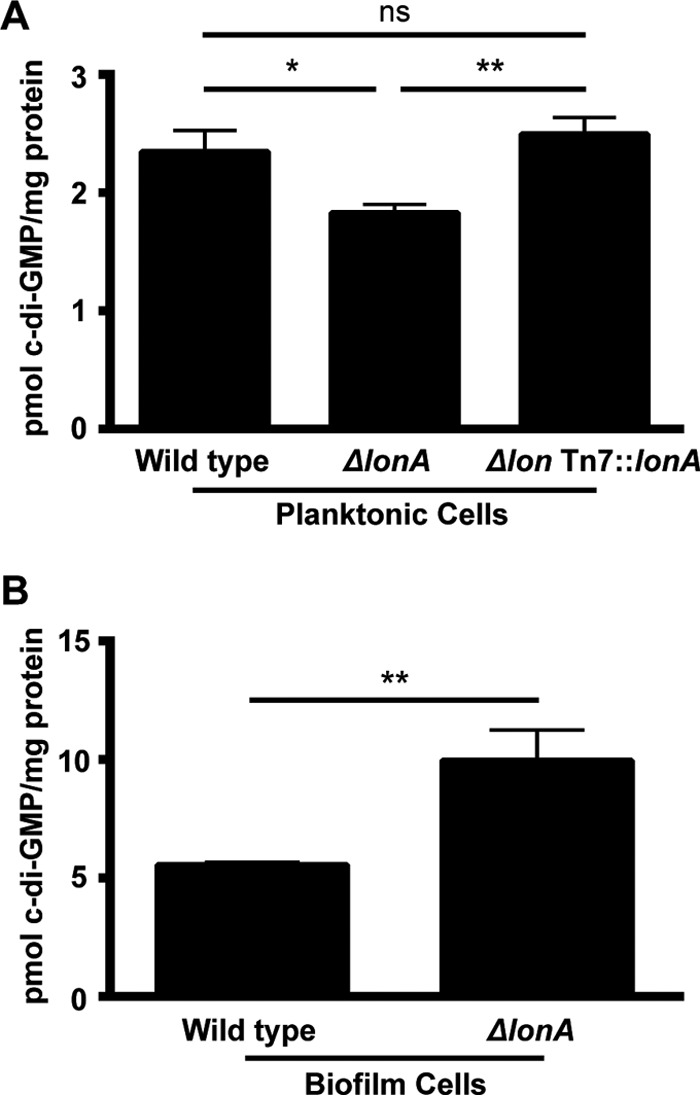
Quantification of intracellular c-di-GMP concentrations. (A) The wild-type, ΔlonA, and lonA-complemented strains were grown aerobically to an OD600 of ∼0.4 before c-di-GMP was extracted from whole-cell protein and quantified by high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS). (B) Wild-type and ΔlonA biofilms were grown in silicone tubing under constant flow for 24 h before being collected for c-di-GMP extraction and quantification by HPLC-MS/MS. The error bars indicate the standard deviations of the results from 3 biological replicates. *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.005 by Student's t test; ns, differences were not significant.
LonA affects the transcriptome of V. cholerae.
LonA is known to regulate various transcriptional regulators in other bacterial organisms (40). We hypothesized that a similar regulation may exist in V. cholerae, in which a negative regulator of biofilm formation, positive regulator of motility, or phosphodiesterase involved in c-di-GMP degradation may be a target protein of LonA in V. cholerae. To understand whether LonA affects transcription at the whole-genome level and whether these transcriptional changes may provide clues regarding the targets of LonA protease, we performed whole-genome-level transcriptional profiling experiments and compared the transcriptomes of the planktonic ΔlonA mutant and wild-type strains.
Analysis of the whole-genome expression data revealed that the expression of 45 genes was significantly upregulated, and the expression of 17 genes was significantly downregulated, in the ΔlonA mutant compared to the wild-type strain by at least 1.5-fold (Table 2). This finding suggests that the stability of transcriptional regulators may be altered in the ΔlonA mutant.
TABLE 2.
Genes that are differentially expressed in the ΔlonA mutant compared to the wild-type straina
| Gene ID by cellular role category | Specific role(s), gene | Fold change (Δlon mutant/WT) |
|---|---|---|
| Pathogenesis | ||
| VC0828 | Toxin-coregulated pilin, tcpA | 2.46 |
| VC0830 | Toxin-coregulated pilus biosynthesis protein Q, tcpQ | 1.81 |
| VC0831 | Toxin-coregulated pilus biosynthesis outer membrane protein C, tcpC | 1.68 |
| VC0832 | Toxin-coregulated pilus biosynthesis protein R, tcpR | 1.99 |
| VC0833 | Toxin-coregulated pilus biosynthesis protein D, tcpD | 1.87 |
| VC0834 | Toxin-coregulated pilus biosynthesis protein S, tcpS | 1.84 |
| VC0837 | Toxin-coregulated pilus biosynthesis protein F, tcpF | 1.66 |
| VC0838 | TCP pilus virulence regulatory protein, tcpN or toxT | 1.72 |
| VC1456 | Cholera enterotoxin B subunit, ctxB | 2.68 |
| VC1457 | Cholera enterotoxin A subunit, ctxA | 2.25 |
| VCA0219 | Hemolysin, hlyA | 2.38 |
| Secretion | ||
| VC1415 | Type VI secretion system, Hcp protein, hcp-1 | 4.80 |
| VCA0017 | Type VI secretion system, Hcp protein, hcp-2 | 5.29 |
| VCA0021 | Type VI secretion system, T6SS immunity, tsiV2 | 1.52 |
| VCA0108 | Type VI secretion system, conserved hypothetical protein, vipB | 1.53 |
| VCA0109 | Type VI secretion system, hypothetical protein | 1.84 |
| VCA0112 | Type VI secretion system, hypothetical protein, fha | 1.70 |
| VCA0114 | Type VI secretion system, hypothetical protein, vasE | 1.52 |
| VCA0124 | Type VI secretion system, T6SS immunity, tsiV3 | 2.32 |
| VPS and biofilm matrix biosynthesis | ||
| VC0916 | Phosphotyrosine protein phosphatase, vpsU | 0.62 |
| VC0918 | UDP-N-acetyl-d-mannosaminuronic acid dehydrogenase, vpsB | 0.50 |
| VC0919 | Serine acetyltransferase-related protein, vpsC | 0.53 |
| VC0926 | Exopolysaccharide, hypothetical protein, vpsJ | 0.54 |
| VC0928 | Matrix proteins, hypothetical protein, rbmA | 0.52 |
| VC0930 | Matrix proteins, hemolysin-related protein, rbmC | 0.52 |
| VC0932 | Matrix proteins, hypothetical protein, rbmE | 0.57 |
| VC0933 | Matrix proteins, hypothetical protein, rbmF | 0.51 |
| VC0935 | Exopolysaccharide, hypothetical protein, vpsM | 0.37 |
| VC1888 | Matrix proteins, hemolysin-related protein, bap1 | 0.50 |
| Metabolism | ||
| VC1516 | Iron-sulfur cluster-binding protein | 0.60 |
| VCA0013 | Maltodextrin phosphorylase, malP | 1.94 |
| VCA0014 | 4-Alpha-glucanotransferase, malQ | 4.26 |
| VCA0016 | 1,4-Alpha-glucan-branching enzyme, glgB | 2.72 |
| VCA0523 | Aminotransferase class II | 1.73 |
| Protein fate | ||
| VC0018 | 16-kDa heat shock protein A, ibpA | 1.70 |
| VC1674 | Periplasmic linker protein, putative | 0.52 |
| VC2675 | Protease HslVU, subunit HslV, hslV | 1.52 |
| Transport and binding proteins | ||
| VC1927 | C4-dicarboxylate transport protein, dctM | 1.91 |
| VC2081 | Zinc ABC transporter, periplasmic zinc-binding protein, znuA | 0.61 |
| VCA0943 | Maltose ABC transporter, permease protein, malG | 2.15 |
| VCA0945 | Maltose ABC transporter, periplasmic maltose-binding protein, malE | 4.23 |
| VCA1028 | Maltoporin, ompS | 4.04 |
| Hypothetical proteins | ||
| VC0102 | Hypothetical protein | 1.72 |
| VC0191 | Conserved hypothetical protein | 2.24 |
| VC0353 | Conserved hypothetical protein | 2.01 |
| VC0469 | Conserved hypothetical protein | 1.55 |
| VC1151 | Conserved hypothetical protein | 0.60 |
| VC1191 | Hypothetical protein | 1.50 |
| VC1262 | Hypothetical protein | 3.65 |
| VC1510 | Hypothetical protein | 0.57 |
| VC2473 | Conserved hypothetical protein | 1.84 |
| VCA0883 | Hypothetical protein | 1.81 |
| VCA1065 | Conserved hypothetical protein | 1.87 |
| Other functions | ||
| VC0175 | Deoxycytidylate deaminase-related protein | 1.67 |
| VC1185 | GGDEF family protein | 0.60 |
| VC1413 | Methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein | 0.56 |
| VC1935 | CDP-diacylglycerol–glycerol-3-phosphate 3-phosphatidyltransferase-related protein | 1.81 |
| VC2389 | Carbamoyl-phosphate synthase, large subunit, carB | 2.20 |
| VC2390 | Carbamoyl -phosphate synthase, small subunit, carA | 1.91 |
| VC2749 | Nitrogen regulation protein NR(I), ntrC | 1.50 |
| VCA1027 | Maltose operon periplasmic protein, putative | 1.84 |
| VCA1069 | Methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein | 2.19 |
Differentially expressed genes were determined using SAM software with a ≥1.5-fold change in gene expression and an FDR of ≤0.03 as the criteria. ID, identifier; WT, wild type.
Expression of biofilm matrix genes is altered in planktonic and biofilm cells of a ΔlonA mutant.
We found that the message abundance of 10 genes that are involved in VPS and biofilm matrix production was lower in the ΔlonA mutant than in the wild type. Similarly, levels of VC1185, a gene encoding a GGDEF family protein that may act as a DGC, was decreased in the ΔlonA mutant. These findings suggest that the decrease in the expression of vps and biofilm matrix genes and VC1185 may be due to the decreased c-di-GMP levels observed in planktonic cells of the ΔlonA mutant.
In light of the whole-genome expression results, which suggest that the expression of vps and matrix protein genes is downregulated in planktonic cells of the ΔlonA mutant, and the abnormal biofilm structure phenotype of the mutant, we hypothesized that the transcriptional regulation of the master biofilm regulators might be impacted by the absence of LonA. To test this hypothesis, we evaluated the expression of vpsL, vpsR, vpsT, and hapR using transcriptional fusions to the lux operon (luxCDABE) carried on a plasmid. Luminescence assays were first conducted in the wild-type and ΔlonA mutant strains from exponentially growing planktonic cells. The expression of vpsL in the ΔlonA mutant was decreased compared to that in the wild type, in agreement with the downregulation of vps genes seen in the whole-genome expression results (Fig. 4A and Table 2). Both vpsR and hapR expression did not change significantly between the two strains, while vpsT expression had a small but significant decrease in the ΔlonA mutant (Fig. 4A).
FIG 4.
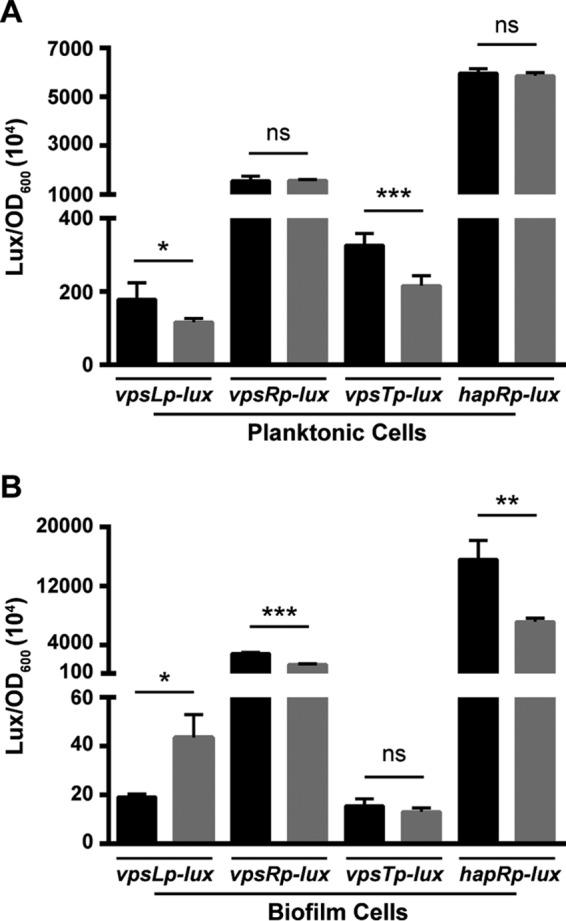
Analysis of biofilm gene expression in the wild-type and ΔlonA strains. Transcriptional reporters harboring regulatory regions of vpsL, vpsR, vpsT, and hapR upstream of a promoterless lux reporter were used to analyze the expression of key biofilm genes. (A) Cultures of the wild-type and ΔlonA strains containing PvpsL-lux, PvpsR-lux, PvpsT-lux, or PhapR-lux were grown to exponential phase (OD600, ∼0.3), and luminescence was measured. (B) Biofilms of the wild-type and ΔlonA strains containing PvpsL-lux, PvpsR-lux, PvpsT-lux, or PhapR-lux were grown for 24 h before luminescence was measured. The black bars represent the wild type, and the gray bars represent the ΔlonA mutant. The graphs present the average numbers of relative light units (RLU) and standard deviations obtained from four technical replicates of two independent biological samples. *, P ≤ 0.01; **, P ≤ 0.001; ***, P ≤ 0.0001 by Student's t test; ns, differences were not significant.
Due to the increase in intracellular c-di-GMP levels in the biofilms of the ΔlonA strain, we also analyzed the expression of vpsL, vpsR, vpsT, and hapR in biofilms of the wild type and the ΔlonA mutant. We found that vpsL expression was significantly increased in ΔlonA biofilms, while vpsR and hapR expression was significantly decreased compared to that in the wild-type strain (Fig. 4B). The expression of vpsT showed no difference between the wild-type and ΔlonA strains (Fig. 4B).
These data confirm that vps genes are being downregulated in planktonic cells of the ΔlonA mutant and reveal that the wild-type patterns of expression for these genes are not fully conserved in a ΔlonA mutant between planktonic and biofilm growth states.
Expression of T6SS genes is increased in the ΔlonA mutant.
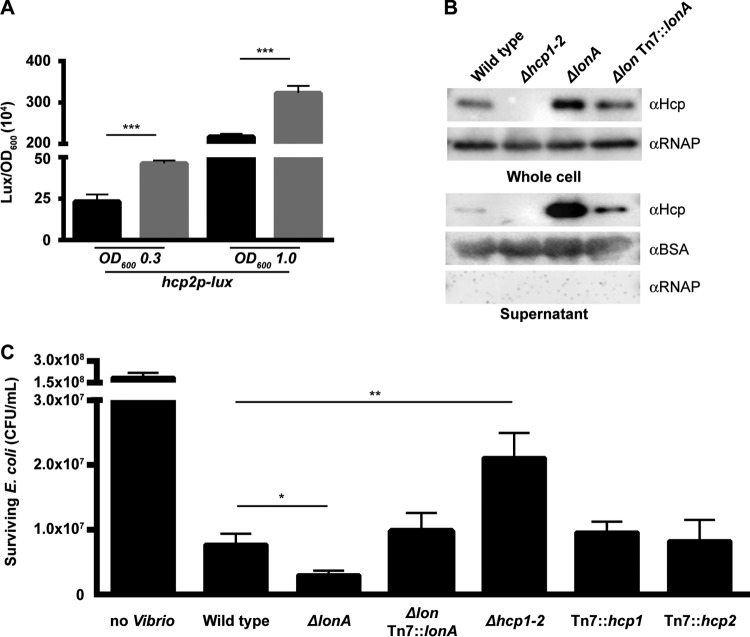
The genes whose expression was upregulated in the ΔlonA mutant included genes involved in biogenesis and function of the type VI secretion system (Table 2), with the hcp1 and hcp2 genes that code for the inner tube proteins of the T6SS being some of the most upregulated genes in the ΔlonA mutant compared to the wild type (Table 2). It was of major interest to us that such a large number of T6SS genes was so highly upregulated in the ΔlonA mutant, as LonA has never been shown to regulate this system in other organisms (Table 2). To further confirm that T6SS genes were upregulated in the ΔlonA mutant, we analyzed hcp expression by using a transcriptional fusion of the hcp2 gene to the lux operon. The luminescence output from Phcp2-lux was found to be significantly higher in the ΔlonA mutant than in the wild type during the exponential and stationary phases of growth (Fig. 5A). This result confirmed that the transcription of genes involved in the T6SS was induced to a higher level in the ΔlonA mutant, but whether or not the system was more active was not addressed.
FIG 5.
Analysis of T6SS expression and activity. (A) The transcriptional reporter harboring the regulatory region of hcp2 upstream of a promoterless lux reporter was used to represent expression of the T6SS. Cultures of the wild-type and ΔlonA strains containing Phcp2-lux were grown aerobically, and luminescence was measured at exponential phase (OD600, ∼0.3) and early stationary phase (OD600, ∼1.0). The graph presents the average numbers of RLU and standard deviations obtained from four technical replicates of two independent biological samples. *, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.0001 by Student's t test. (B) Hcp production and secretion were analyzed in whole-cell and culture supernatants of the wild-type, ΔlonA, and lonA-complemented strains by immunoblotting. Equal amounts of whole-cell protein (determined by BCA assay) were loaded onto a 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gel to analyze production. Prior to TCA precipitation and total protein quantification, 100 μg/ml BSA was added to the supernatant. Equal volumes of TCA-precipitated protein were loaded onto a 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gel to analyze secretion. The blots were probed for Hcp, while duplicate blots were probed for RNAPα and BSA. The data shown are representative of the results from three independent experiments. (C) Interbacterial killing was analyzed by mixing V. cholerae strains and prey E. coli strain MC4100 in a 10:1 ratio, incubating them on LB agar plates containing 340 mM NaCl for 4 h at 30°C, and quantifying the surviving E. coli MC4100 cells. The data represent the averages and standard deviations of the results from three biological replicates. *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.005 by Student's t test.
To determine if more Hcp was actually being produced by the ΔlonA mutant, we analyzed Hcp production by Western blotting using whole-cell and supernatant protein samples. We found that a greater amount of Hcp was present in both the whole-cell and supernatant samples of the ΔlonA mutant than in the wild type, while complementation of the ΔlonA mutant restored Hcp to wild-type levels (Fig. 5B). A Δhcp1 Δhcp2 mutant was included as a negative control, as it is unable to produce Hcp (28). As expected, no Hcp was detectable in the samples collected from this mutant.
In order to determine if the activity of the T6SS system was affected in the ΔlonA mutant, we carried out an interbacterial killing assay in which E. coli was used as prey for T6SS-mediated killing by V. cholerae. We found that the level of surviving E. coli strain MC4100 was modestly but significantly lower in the ΔlonA mutant than that in the wild type (Fig. 5C). This finding suggests that LonA affects the transcription, production, and activity of the T6SS.
Expression of virulence genes is increased in the ΔlonA mutant, and LonA plays a role in colonization of the infant mouse.
The message abundance of virulence regulators toxT and ctxAB and of most of the genes responsible for TCP production was also significantly higher in the ΔlonA mutant (Table 2). Due to a multitude of virulence-related genes being upregulated in the ΔlonA mutant and LonA having been shown to play a role in the virulence of many bacterial species, we wanted to determine if LonA plays a role in the virulence of V. cholerae (Table 2). We first chose ctxA and tcpA, genes essential for the production of CT and TCP, respectively, as representatives of the virulence genes that were upregulated in the expression profiling study and analyzed their expression using lux transcriptional fusions. Both ctxA and tcpA, in agreement with the expression profiling data, were significantly upregulated in the ΔlonA mutant compared to the wild type during both exponential- and stationary-phase growth (Fig. 6A).
FIG 6.
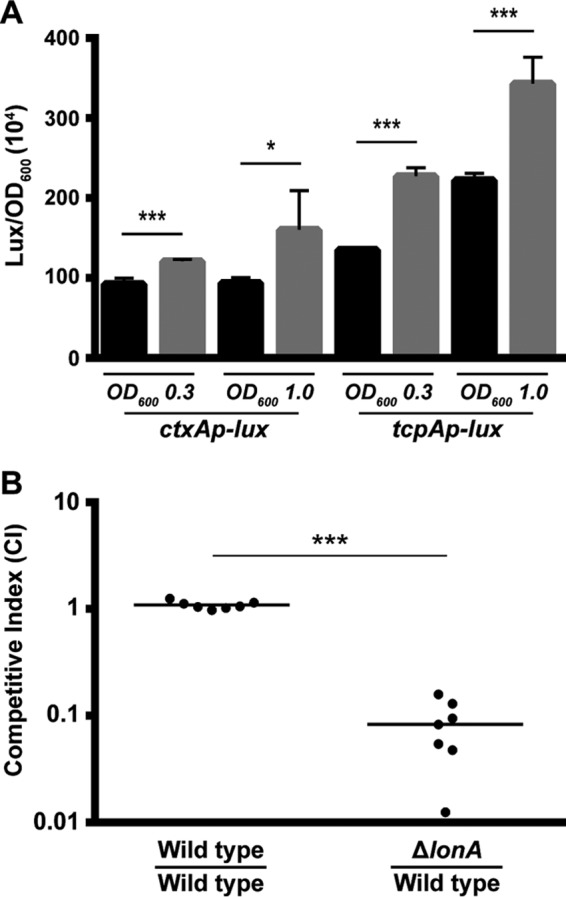
Analysis of virulence gene expression and intestinal colonization of the ΔlonA mutant. (A) Transcriptional reporters harboring regulatory regions of ctxA and tcpA upstream of a promoterless lux reporter were used to represent the expression of key virulence genes. Cultures of the wild-type and ΔlonA strains containing PctxA-lux or PtcpA-lux were grown aerobically to exponential phase (OD600, ∼0.3) and early stationary phase (OD600, ∼1.0), and luminescence was measured. The graph presents the average numbers of RLU and standard deviations obtained from four technical replicates of two independent biological samples. *, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.0001 by Student's t test. (B) The wild-type strain was coinoculated with a ΔlonA mutant at a ratio of ∼1:1 into infant mice. The number of bacteria per intestine was determined 20 to 22 h postinoculation. The competitive index (CI) was determined as the output ratio of mutant to wild-type cells divided by the input ratio of mutant to wild-type cells. Each point represents results from an individual mouse. Statistical analysis was carried out using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test, comparing the CI of each strain to the CI of the wild-type lacZ+ strain divided by the CI of the wild-type lacZ-negative strain.
The overexpression of virulence genes in the ΔlonA mutant suggested that it may have the ability to outcompete the wild type in an infection setting. To test this hypothesis, we assessed the ability of the ΔlonA mutant to colonize the infant mouse intestine by competing it with the wild-type strain. The ΔlonA mutant was found to be severely defective in colonizing the infant mouse, with a competitive index of 0.08 (Fig. 6B). To ensure that any defect in colonization observed by analysis of the ΔlonA mutant was dependent on the environment of the host's digestive tract, we competed the strains in vitro with the same strain mixture used for the infection studies. The output ratios of the in vitro competitions were found to be the same as the input ratios (data not shown). This result suggests that LonA controls the processes involved in the virulence of V. cholerae.
DISCUSSION
The body of research addressing the roles of the enigmatic Lon protease has continued to develop since it was first described as a regulator of capsular polysaccharide production in E. coli in 1963 (50). Our understanding of LonA's regulatory repertoire has since grown to include a wide array of cellular processes in bacteria, including cell division, the SOS response, quorum sensing, motility, biofilm formation, and virulence (51–61). The observations reported here serve not only to characterize the roles of LonA in V. cholerae but also to expand the available knowledge of the regulatory roles of LonA in bacteria. We have determined that a ΔlonA mutant of V. cholerae displays alterations in cell morphology, biofilm, motility, and virulence phenotypes similar to and different from those of ΔlonA mutants in other bacterial species. Additionally, we show for the first time that this protease is involved in the regulation of global c-di-GMP pools and the T6SS.
While using a transposon mutant library of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to find mutants defective for biofilm formation with and without the presence of a sub-MIC of gentamicin, Marr et al. found that insertions in the lonA gene drastically reduced the ability of the organism to form a biofilm (56). Our assessment of the biofilm-forming capacities of a V. cholerae ΔlonA mutant under constant-flow conditions revealed that the mutant formed biofilms with abnormal characteristics compared to those of the wild-type strain, accompanied by a significant defect in accumulated biomass after 48 h of growth. The decrease in biofilm density exhibited by the ΔlonA mutant suggests that adhesion between cells in the biofilm has been compromised. The elongated cell morphology apparent within the ΔlonA mutant biofilm may be a contributing factor to the porous biofilm phenotype, although the specific characteristics of the biofilm that would be affected by this filamentous cell type are unclear. We also observed that levels of c-di-GMP and vpsL expression were decreased in planktonic cells and increased in biofilm cells of the ΔlonA mutant. Higher vpsL expression would suggest that the ΔlonA mutant should be able to produce more VPS and thus exhibit an enhanced ability to form biofilms. However, the biofilms produced by the ΔlonA mutant were structurally quite different than those of the wild type, leading us to believe that both the structure of biofilms and the c-di-GMP-mediated regulation of biofilm formation are compromised in the absence of LonA.
Due to the presence of significant alterations in biofilm phenotype, cellular c-di-GMP levels, and message abundance of biofilm matrix genes in the ΔlonA mutant, we reasoned that one or more of the three master regulators of biofilm formation, VpsR, VpsT, and HapR, may be impacted. We found that in planktonic cells, the expression of biofilm genes and vpsT was significantly decreased in the ΔlonA mutant, while the expression of vpsR and hapR was not altered. It is possible that the modest decrease in global c-di-GMP levels in planktonic ΔlonA mutant cells is the sole factor in the downregulation of these biofilm genes, as the level of intracellular c-di-GMP is directly linked to the induction of these genes through direct binding to VpsT, whose activity is controlled by cellular levels of c-di-GMP (62). It remains to be determined if VpsT or a PDE is a target of LonA. We determined that in biofilms of the ΔlonA mutant, the expression of biofilm matrix genes was increased, vpsR and hapR expression was decreased, and vpsT expression was not altered compared to that in the wild type. We previously showed that wild-type V. cholerae responds to an increase in c-di-GMP levels with an increase in vpsL, vpsT, and vpsR expression (46). While the ΔlonA mutant is still able to increase vpsL expression when there is an increase in c-di-GMP, the lack of an increase in vpsR and vpsT expression further supports that c-di-GMP-mediated regulation of biofilm formation is altered significantly in the absence of LonA. It is unclear how vpsL expression is being increased in the ΔlonA mutant, but it is possible that the decrease in hapR expression, a negative regulator of vpsL, allows the observed increase in vpsL expression (12). Taken together, these expression data reveal that LonA is required for the full complement of transcriptional regulation that is characteristic of the switch from planktonic to biofilm growth states in V. cholerae. Future studies are planned to determine if VpsR, VpsT, or other regulators of V. cholerae biofilm formation are direct targets of LonA.
To date, the effects of the Lon protease on biofilm formation in bacteria have been studied only in P. aeruginosa and V. cholerae (this work and reference 56). In these two organisms, the contribution of LonA differs, in that P. aeruginosa ΔlonA mutants exhibit a severe defect in biofilm formation, while V. cholerae ΔlonA mutants still produce biofilms but with compromised structure (56). The exact mechanism by which lonA regulates these processes remains to be determined.
The regulation of motility by the Lon protease has been well studied. In Proteus mirabilis, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and P. aeruginosa, the Lon protease has been found to affect swarming motility (54–56). Additionally, in P. aeruginosa, LonA has been shown to affect swimming and twitching motility. While the mechanisms for these effects are not clear, it is interesting to note that in the absence of the Lon protease, all motility behaviors are inhibited (56, 59). In contrast, swarming motility behaviors of Bacillus subtilis and P. mirabilis are upregulated in the absence of LonA. A recent study by Mukherjee and colleagues (63) described a system present in B. subtilis in which LonA inhibits swarming motility by degrading SwrA, the master activator of swarming motility in that species, an event requiring the novel substrate-specific adaptor protein SmiA. In the case of P. mirabilis, it was found that cells deficient in LonA had a hyperswarming phenotype due to increased stabilization of the swarming activators FlhDC (55). It is not entirely clear what LonA might be targeting in V. cholerae to alter motility. The absence of LonA may lead to the stabilization of an activator of the flagellar regulatory cascade in a fashion similar to that of FlhDC stabilization, but we found no evidence of differential regulation of the flagellar regulatory cascade between the wild-type and ΔlonA mutant strain. It may be that LonA affects motility in V. cholerae in an entirely transcriptionally independent manner. As motility is negatively regulated by c-di-GMP, the decrease in c-di-GMP levels in planktonic ΔlonA cells may be responsible for the increased motility phenotype. If this is the case, LonA may be targeting the enzymes or regulators of the enzymes that synthesize and degrade c-di-GMP. A number of these enzymes, known as diguanylate cyclases (DGCs) and phosphodiesterases (PDEs), have been shown to affect the motility of V. cholerae in a c-di-GMP-dependent manner (43).
To our knowledge, all ΔlonA mutants assessed for virulence capabilities in standard in vivo models have exhibited a decreased ability to cause infection (57, 58, 60, 61). The upregulation of key virulence genes in a V. cholerae ΔlonA strain that we observed suggested that this organism may exhibit enhanced virulence compared to that of the wild type; yet, when we tested the ability of the ΔlonA strain to compete with the wild type in the infant mouse infection model, we found that it had a severe defect in colonization. It may be that the altered virulence gene expression of the ΔlonA mutant is detrimental when it attempts to survive and colonize the infant mouse small intestine, as it has been shown that genes in the small intestine, such as tcpA and ctxAB, are temporally and spatially regulated during infection (64). Alternatively, it may be that the in vivo fitness of the ΔlonA mutant is compromised and that it lacks the ability to survive host defenses encountered in the infant mouse digestive tract, such as antimicrobial peptides or reactive nitrogen species (65). The inability of the ΔlonA mutant to form a normal biofilm may also affect its ability to survive in the infant mouse small intestine, leading to an inability to compete with the wild type. Tsou et al. (66) showed that the regulation of motility behaviors plays a significant role in the regulation of virulence gene expression during a V. cholerae infection. Therefore, the hypermotile phenotype of the ΔlonA strain may impede this coordinated regulation, leading to a decrease in colonization ability.
There is a precedent for the degradation of virulence regulators by LonA in other species, including the virulence regulators RovA of Yersinia and HilC and HilD of Salmonella (67, 68). Possible candidates for targets of LonA that might upregulate virulence gene expression in V. cholerae when stabilized include AphA, ToxRS, TcpPH, and ToxT. We did not find there to be a statistically significant difference in the amount of HapR produced by the ΔlonA mutant compared to that produced by the wild type (data not shown), so it is unlikely that LonA regulates the virulence genes by targeting a quorum-sensing pathway. Exactly how LonA regulates the CT and TCP pathways in V. cholerae remains to be determined.
Until now, the Lon protease has never been shown to regulate the T6SS. LonA of V. cholerae appears to negatively regulate the transcription of all three gene clusters of the system, the production and secretion of Hcp, and the activity of the system against E. coli prey. We speculate that LonA regulates one of the transcriptional regulators of the T6SS, such as TsrA, VasH, VxrB, or CRP. Hcp was named hemolysin-coregulated protein before the characterization of the T6SS, because it was found to be coregulated with the virulence factor HlyA in an HlyU-dependent manner (69). Because hlyA and both hcp1 and hcp2 were upregulated in the ΔlonA mutant, the winged helix-turn-helix (wHTH) transcriptional regulator HlyU is another intriguing candidate for degradation by LonA (70). While we did not investigate any links between the aberrant biofilm phenotype and the upregulation of T6SS expression and activity in this study, it is interesting that LonA appears to play a regulatory role in both of these systems. Schwarz et al. (71) showed that the T6SS is required for Burkholderia thailandensis to proliferate in a biofilm state when in the presence of Pseudomonas putida, and one study done with V. cholerae showed that T6SS expression and activity are upregulated when V. cholerae is allowed to form a biofilm on chitinous surfaces (71, 72). While these studies do not imply that there is a direct regulatory connection between the T6SS and biofilm formation, they certainly suggest that the two processes are contextually related. Taken together with the LonA-dependent phenotypes we report here, we speculate that there may be some degree of coregulation of biofilm formation and the T6SS in V. cholerae.
Although there is precedence for the direct degradation of transcriptional regulators by the Lon protease, it has yet to be determined whether all of the phenotypes of a ΔlonA mutant of V. cholerae are due to directed proteolysis by LonA. The Lon protease is known to be important for maintaining proper protein homeostasis in E. coli, in which it degrades ∼50% of all damaged proteins (41). Therefore, it is possible that LonA of V. cholerae plays a similar role, and in the absence of this protein quality control, cells become sick due to proteotoxic stress. If ΔlonA mutant cells are highly stressed by the absence of LonA, this might lead to some of the phenotypes we observed, such as compromised biofilm structure and an inability to colonize infant mice. In order to resolve the uncertainty associated with the origins of the phenotypes we have described in a ΔlonA mutant, we plan to carry out further studies, with the hope of identifying regulatory proteins that are degraded directly by LonA.
It is clear that LonA plays an important role in the life cycle of V. cholerae. Although we were not able to reveal any of the specific mechanisms by which LonA regulates biofilm formation, motility, virulence, or the T6SS in V. cholerae, we believe that this work is the first step in understanding the seemingly important role that this intracellular ATP-dependent protease plays in the physiology of this human pathogen.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Benjamin Abrams from the UCSC Life Sciences Microscopy Center for his technical support, Qiangli Zhang for help with the high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS) experiments and analysis, and Jennifer Teschler for her comments on the manuscript.
c-di-GMP quantification was performed at the UCSC Mass Spectrometry Facility, which is funded by NIH grant S10-RR20939 (MS equipment grant).
Footnotes
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JB.00741-15.
REFERENCES
- 1.Teschler JK, Zamorano-Sánchez D, Utada AS, Warner CJA, Wong GCL, Linington RG, Yildiz FH. 2015. Living in the matrix: assembly and control of Vibrio cholerae biofilms. Nat Rev Microbiol 13:255–268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Matz C, McDougald D, Moreno AM, Yung PY, Yildiz FH, Kjelleberg S. 2005. Biofilm formation and phenotypic variation enhance predation-driven persistence of Vibrio cholerae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:16819–16824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0505350102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Tamayo R, Patimalla B, Camilli A. 2010. Growth in a biofilm induces a hyperinfectious phenotype in Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun 78:3560–3569. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00048-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Beyhan S, Yildiz FH. 2007. Smooth to rugose phase variation in Vibrio cholerae can be mediated by a single nucleotide change that targets c-di-GMP signalling pathway. Mol Microbiol 63:995–1007. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05568.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Yildiz FH, Schoolnik GK. 1999. Vibrio cholerae O1 El Tor: identification of a gene cluster required for the rugose colony type, exopolysaccharide production, chlorine resistance, and biofilm formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:4028–4033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.7.4028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yildiz F, Fong J, Sadovskaya I, Grard T, Vinogradov E. 2014. Structural characterization of the extracellular polysaccharide from Vibrio cholerae O1 El-Tor. PLoS One 9:e86751. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Fong JCN, Karplus K, Schoolnik GK, Yildiz FH. 2006. Identification and characterization of RbmA, a novel protein required for the development of rugose colony morphology and biofilm structure in Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol 188:1049–1059. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.3.1049-1059.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Fong JCN, Yildiz FH. 2007. The rbmBCDEF gene cluster modulates development of rugose colony morphology and biofilm formation in Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol 189:2319–2330. doi: 10.1128/JB.01569-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Berk V, Fong JCN, Dempsey GT, Develioglu ON, Zhuang X, Liphardt J, Yildiz FH, Chu S. 2012. Molecular architecture and assembly principles of Vibrio cholerae biofilms. Science 337:236–239. doi: 10.1126/science.1222981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Yildiz FH, Dolganov NA, Schoolnik GK. 2001. VpsR, a member of the response regulators of the two-component regulatory systems, is required for expression of vps biosynthesis genes and EPSETr-associated phenotypes in Vibrio cholerae O1 El Tor. J Bacteriol 183:1716–1726. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.5.1716-1726.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Casper-Lindley C, Yildiz FH. 2004. VpsT is a transcriptional regulator required for expression of vps biosynthesis genes and the development of rugose colonial morphology in Vibrio cholerae O1 El Tor. J Bacteriol 186:1574–1578. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.5.1574-1578.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Waters CM, Lu W, Rabinowitz JD, Bassler BL. 2008. Quorum sensing controls biofilm formation in Vibrio cholerae through modulation of cyclic di-GMP levels and repression of vpsT. J Bacteriol 190:2527–2536. doi: 10.1128/JB.01756-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zamorano-Sánchez D, Fong JCN, Kilic S, Erill I, Yildiz FH. 2015. Identification and characterization of VpsR and VpsT binding sites in Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol 197:1221–1235. doi: 10.1128/JB.02439-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Tischler AD, Camilli A. 2004. Cyclic diguanylate (c-di-GMP) regulates Vibrio cholerae biofilm formation. Mol Microbiol 53:857–869. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04155.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Beyhan S, Tischler AD, Camilli A, Yildiz FH. 2006. Transcriptome and phenotypic responses of Vibrio cholerae to increased cyclic di-GMP level. J Bacteriol 188:3600–3613. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.10.3600-3613.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Römling U, Galperin MY, Gomelsky M. 2013. Cyclic di-GMP: the first 25 years of a universal bacterial second messenger. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 77:1–52. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00043-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Charles RC, Ryan ET. 2011. Cholera in the 21st century. Curr Opin Infect Dis 24:472–477. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0b013e32834a88af. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kovacikova G, Skorupski K. 2002. Regulation of virulence gene expression in Vibrio cholerae by quorum sensing: HapR functions at the aphA promoter. Mol Microbiol 46:1135–1147. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03229.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Krukonis ES, Yu RR, DiRita VJ. 2000. The Vibrio cholerae ToxR/TcpP/ToxT virulence cascade: distinct roles for two membrane-localized transcriptional activators on a single promoter. Mol Microbiol 38:67–84. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.02111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.DiRita VJ, Parsot C, Jander G, Mekalanos JJ. 1991. Regulatory cascade controls virulence in Vibrio cholerae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88:5403–5407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pukatzki S, Ma AT, Sturtevant D, Krastins B, Sarracino D, Nelson WC, Heidelberg JF, Mekalanos JJ. 2006. Identification of a conserved bacterial protein secretion system in Vibrio cholerae using the Dictyostelium host model system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:1528–1533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0510322103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ho BT, Dong TG, Mekalanos JJ. 2014. A view to a kill: the bacterial type VI secretion system. Cell Host Microbe 15:9–21. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2013.11.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Pukatzki S, Ma AT, Revel AT, Sturtevant D, Mekalanos JJ. 2007. Type VI secretion system translocates a phage tail spike-like protein into target cells where it cross-links actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:15508–15513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0706532104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Basler M, Pilhofer M, Henderson GP, Jensen GJ, Mekalanos JJ. 2012. Type VI secretion requires a dynamic contractile phage tail-like structure. Nature 483:182–186. doi: 10.1038/nature10846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zheng J, Ho B, Mekalanos JJ. 2011. Genetic analysis of anti-amoebae and anti-bacterial activities of the type VI secretion system in Vibrio cholerae. PLoS One 6:e23876. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ishikawa T, Rompikuntal PK, Lindmark B, Milton DL, Wai SN. 2009. Quorum sensing regulation of the two hcp alleles in Vibrio cholerae O1 strains. PLoS One 4:e6734. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zheng J, Shin OS, Cameron DE, Mekalanos JJ. 2010. Quorum sensing and a global regulator TsrA control expression of type VI secretion and virulence in Vibrio cholerae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:21128–21133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1014998107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Cheng AT, Ottemann KM, Yildiz FH. 2015. Vibrio cholerae response regulator VxrB controls colonization and regulates the type VI secretion system. PLoS Pathog 11:e1004933. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kitaoka M, Miyata ST, Brooks TM, Unterweger D, Pukatzki S. 2011. VasH is a transcriptional regulator of the type VI secretion system functional in endemic and pandemic Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol 193:6471–6482. doi: 10.1128/JB.05414-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ishikawa T, Sabharwal D, Bröms J, Milton DL, Sjöstedt A, Uhlin BE, Wai SN. 2012. Pathoadaptive conditional regulation of the type VI secretion system in Vibrio cholerae O1 strains. Infect Immun 80:575–584. doi: 10.1128/IAI.05510-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Syed KA, Beyhan S, Correa N, Queen J, Liu J, Peng F, Satchell KJF, Yildiz F, Klose KE. 2009. The Vibrio cholerae flagellar regulatory hierarchy controls expression of virulence factors. J Bacteriol 191:6555–6570. doi: 10.1128/JB.00949-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Papenfort K, Förstner KU, Cong J-P, Sharma CM, Bassler BL. 2015. Differential RNA-seq of Vibrio cholerae identifies the VqmR small RNA as a regulator of biofilm formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:E766–E775. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1500203112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Song T, Sabharwal D, Gurung JM, Cheng AT, Sjöström AE, Yildiz FH, Uhlin BE, Wai SN. 2014. Vibrio cholerae utilizes direct sRNA regulation in expression of a biofilm matrix protein. PLoS One 9:e101280. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Shao Y, Bassler BL. 2014. Quorum regulatory small RNAs repress type VI secretion in Vibrio cholerae. Mol Microbiol 92:921–930. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lenz DH, Mok KC, Lilley BN, Kulkarni RV, Wingreen NS, Bassler BL. 2004. The small RNA chaperone Hfq and multiple small RNAs control quorum sensing in Vibrio harveyi and Vibrio cholerae. Cell 118:69–82. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.06.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Matson JS, DiRita VJ. 2005. Degradation of the membrane-localized virulence activator TcpP by the YaeL protease in Vibrio cholerae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:16403–16408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0505818102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Teoh WP, Matson JS, DiRita VJ. 2015. Regulated intramembrane proteolysis of the virulence activator TcpP in Vibrio cholerae is initiated by the tail-specific protease (Tsp). Mol Microbiol 97:822–831. doi: 10.1111/mmi.13069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Almagro-Moreno S, Kim TK, Skorupski K, Taylor RK. 2015. Proteolysis of virulence regulator ToxR is associated with entry of Vibrio cholerae into a dormant state. PLoS Genet 11:e1005145. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Gur E. 2013. The Lon AAA+ protease, p 35–51. In Dougan DA. (ed), Regulated proteolysis in microorganisms. Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht, the Netherlands. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Van Melderen L, Aertsen A. 2009. Regulation and quality control by Lon-dependent proteolysis. Res Microbiol 160:645–651. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2009.08.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Gottesman S. 1996. Proteases and their targets in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet 30:465–506. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genet.30.1.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.National Research Council, Committee for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2011. Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals, 8th ed National Academies Press, Washington, DC: https://grants.nih.gov/grants/olaw/Guide-for-the-Care-and-use-of-laboratory-animals.pdf. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Liu X, Beyhan S, Lim B, Linington RG, Yildiz FH. 2010. Identification and characterization of a phosphodiesterase that inversely regulates motility and biofilm formation in Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol 192:4541–4552. doi: 10.1128/JB.00209-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Bilecen K, Fong JCN, Cheng A, Jones CJ, Zamorano-Sánchez D, Yildiz FH. 2015. Polymyxin B resistance and biofilm formation in Vibrio cholerae are controlled by the response regulator CarR. Infect Immun 83:1199–1209. doi: 10.1128/IAI.02700-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Heydorn A, Nielsen AT, Hentzer M, Sternberg C, Givskov M, Ersbøll BK, Molin S. 2000. Quantification of biofilm structures by the novel computer program COMSTAT. Microbiology 146(Part 10):2395–2407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Beyhan S, Tischler AD, Camilli A, Yildiz FH. 2006. Differences in gene expression between the classical and El Tor biotypes of Vibrio cholerae O1. Infect Immun 74:3633–3642. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01750-05. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Gentleman RC, Carey VJ, Bates DM, Bolstad B, Dettling M, Dudoit S, Ellis B, Gautier L, Ge Y, Gentry J, Hornik K, Hothorn T, Huber W, Iacus S, Irizarry R, Leisch F, Li C, Maechler M, Rossini AJ, Sawitzki G, Smith C, Smyth G, Tierney L, Yang JY, Zhang J. 2004. Bioconductor: open software development for computational biology and bioinformatics. Genome Biol 5:R80. doi: 10.1186/gb-2004-5-10-r80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Tusher VG, Tibshirani R, Chu G. 2001. Significance analysis of microarrays applied to the ionizing radiation response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:5116–5121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.091062498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Taylor RK, Miller VL, Furlong DB, Mekalanos JJ. 1987. Use of phoA gene fusions to identify a pilus colonization factor coordinately regulated with cholera toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 84:2833–2837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Markovitz A. 1964. Regulatory mechanisms for synthesis of capsular polysaccharide in mucoid mutants of Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 51:239–246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.2.239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Jonas K, Liu J, Chien P, Laub MT. 2013. Proteotoxic stress induces a cell cycle arrest by stimulating Lon to degrade the replication initiator DnaA. Cell 154:623–636. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.06.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Mizusawa S, Gottesman S. 1983. Protein degradation in Escherichia coli: the lon gene controls the stability of sulA protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 80:358–362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Takaya A, Tabuchi F, Tsuchiya H, Isogai E, Yamamoto T. 2008. Negative regulation of quorum-sensing systems in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by ATP-dependent Lon protease. J Bacteriol 190:4181–4188. doi: 10.1128/JB.01873-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Stewart BJ, Enos-Berlage JL, McCarter LL. 1997. The lonS gene regulates swarmer cell differentiation of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Bacteriol 179:107–114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Clemmer KM, Rather PN. 2008. The Lon protease regulates swarming motility and virulence gene expression in Proteus mirabilis. J Med Microbiol 57:931–937. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.47778-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Marr AK, Overhage J, Bains M, Hancock REW. 2007. The Lon protease of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is induced by aminoglycosides and is involved in biofilm formation and motility. Microbiology 153:474–482. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2006/002519-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Takaya A, Suzuki M, Matsui H, Tomoyasu T, Sashinami H, Nakane A, Yamamoto T. 2003. Lon, a stress-induced ATP-dependent protease, is critically important for systemic Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium infection of mice. Infect Immun 71:690–696. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.2.690-696.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Robertson GT, Kovach ME, Allen CA, Ficht TA, Roop RM Jr. 2000. The Brucella abortus Lon functions as a generalized stress response protease and is required for wild-type virulence in BALB/c mice. Mol Microbiol 35:577–588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Breidenstein EBM, Janot L, Strehmel J, Fernandez L, Taylor PK, Kukavica-Ibrulj I, Gellatly SL, Levesque RC, Overhage J, Hancock REW. 2012. The Lon protease is essential for full virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS One 7:e49123. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Lan L, Deng X, Xiao Y, Zhou J-M, Tang X. 2007. Mutation of Lon protease differentially affects the expression of Pseudomonas syringae type III secretion system genes in rich and minimal media and reduces pathogenicity. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 20:682–696. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-20-6-0682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Su S, Stephens BB, Alexandre G, Farrand SK. 2006. Lon protease of the α-proteobacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens is required for normal growth, cellular morphology and full virulence. Microbiology 152:1197–1207. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.28657-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Krasteva PV, Fong JCN, Shikuma NJ, Beyhan S, Navarro MVAS, Yildiz FH, Sondermann H. 2010. Vibrio cholerae VpsT regulates matrix production and motility by directly sensing cyclic di-GMP. Science 327:866–868. doi: 10.1126/science.1181185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Mukherjee S, Bree AC, Liu J, Patrick JE, Chien P, Kearns DB. 2015. Adaptor-mediated Lon proteolysis restricts Bacillus subtilis hyperflagellation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:250–255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1417419112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Lee SH, Hava DL, Waldor MK, Camilli A. 1999. Regulation and temporal expression patterns of Vibrio cholerae virulence genes during infection. Cell 99:625–634. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81551-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Davies BW, Bogard RW, Dupes NM, Gerstenfeld TAI, Simmons LA, Mekalanos JJ. 2011. DNA damage and reactive nitrogen species are barriers to Vibrio cholerae colonization of the infant mouse intestine. PLoS Pathog 7:e1001295. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Tsou AM, Frey EM, Hsiao A, Liu Z, Zhu J. 2008. Coordinated regulation of virulence by quorum sensing and motility pathways during the initial stages of Vibrio cholerae infection. Commun Integr Biol 1:42–44. doi: 10.4161/cib.1.1.6662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Herbst K, Bujara M, Heroven AK, Opitz W, Weichert M, Zimmermann A, Dersch P. 2009. Intrinsic thermal sensing controls proteolysis of Yersinia virulence regulator RovA. PLoS Pathog 5:e1000435. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Takaya A, Kubota Y, Isogai E, Yamamoto T. 2005. Degradation of the HilC and HilD regulator proteins by ATP-dependent Lon protease leads to downregulation of Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 gene expression. Mol Microbiol 55:839–852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Williams SG, Varcoe LT, Attridge SR, Manning PA. 1996. Vibrio cholerae Hcp, a secreted protein coregulated with HlyA. Infect Immun 64:283–289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Mukherjee D, Datta AB, Chakrabarti P. 2014. Crystal structure of HlyU, the hemolysin gene transcription activator, from Vibrio cholerae N16961 and functional implications. Biochim Biophys Acta 1844:2346–2354. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2014.09.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Schwarz S, West TE, Boyer F, Chiang W-C, Carl MA, Hood RD, Rohmer L, Tolker-Nielsen T, Skerrett SJ, Mougous JD. 2010. Burkholderia type VI secretion systems have distinct roles in eukaryotic and bacterial cell interactions. PLoS Pathog 6:e1001068. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Borgeaud S, Metzger LC, Scrignari T, Blokesch M. 2015. The type VI secretion system of Vibrio cholerae fosters horizontal gene transfer. Science 347:63–67. doi: 10.1126/science.1260064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.