FIG 6.
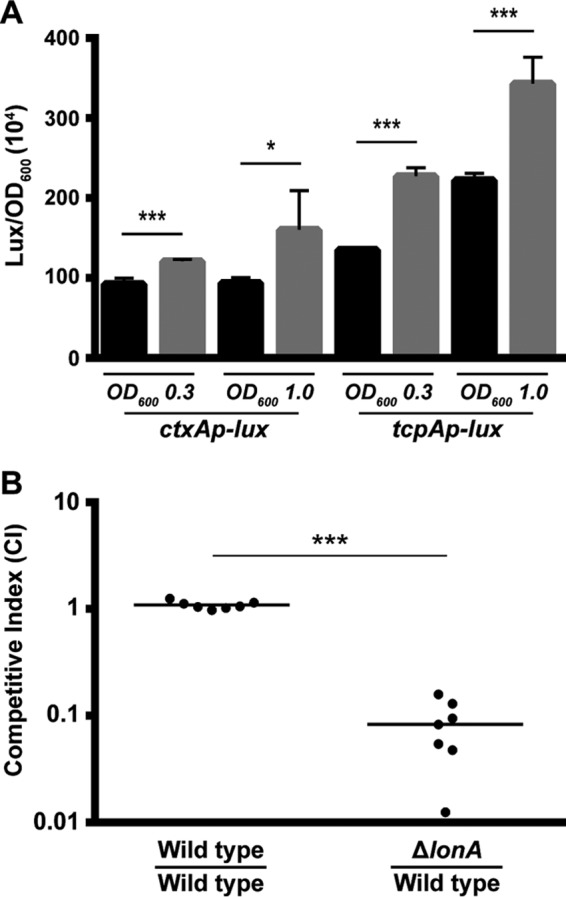
Analysis of virulence gene expression and intestinal colonization of the ΔlonA mutant. (A) Transcriptional reporters harboring regulatory regions of ctxA and tcpA upstream of a promoterless lux reporter were used to represent the expression of key virulence genes. Cultures of the wild-type and ΔlonA strains containing PctxA-lux or PtcpA-lux were grown aerobically to exponential phase (OD600, ∼0.3) and early stationary phase (OD600, ∼1.0), and luminescence was measured. The graph presents the average numbers of RLU and standard deviations obtained from four technical replicates of two independent biological samples. *, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.0001 by Student's t test. (B) The wild-type strain was coinoculated with a ΔlonA mutant at a ratio of ∼1:1 into infant mice. The number of bacteria per intestine was determined 20 to 22 h postinoculation. The competitive index (CI) was determined as the output ratio of mutant to wild-type cells divided by the input ratio of mutant to wild-type cells. Each point represents results from an individual mouse. Statistical analysis was carried out using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test, comparing the CI of each strain to the CI of the wild-type lacZ+ strain divided by the CI of the wild-type lacZ-negative strain.
