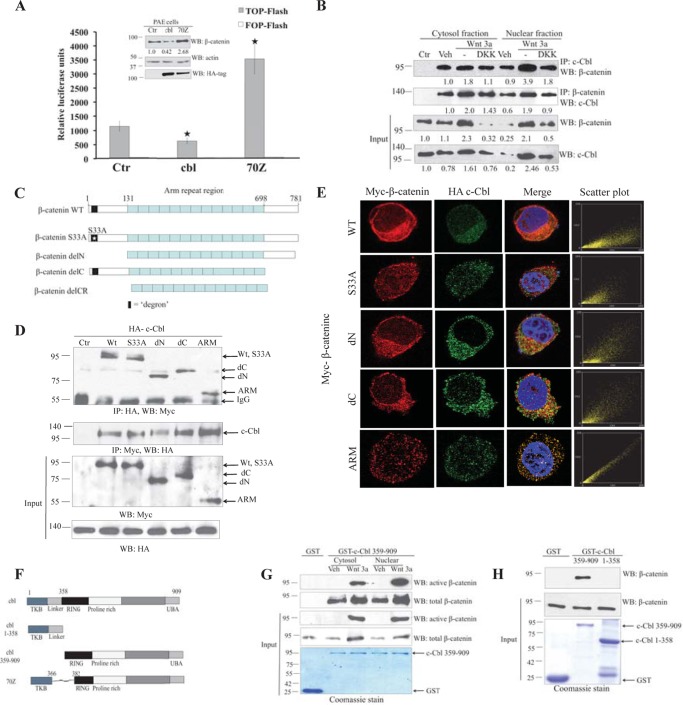
FIGURE 1.
Direct interaction of c-Cbl and β-catenin in ECs independent of Wnt status. A, differential Wnt activity in c-Cbl and c-Cbl-70Z expressing PAECs. Cell lysates of PAECs stably expressing HA-tagged c-Cbl or c-Cbl-70Z and TCF-responsive promoter-reporter pBAR and nonresponsive control (Ctr) reporter pfuBAR tethered to the luciferase reporter (20) were analyzed for luciferase assay. Activity of the Wnt signaling pathway is quantified by measuring relative firefly luciferase units normalized to protein concentration. Mean results of three experiments are shown. Student's t test was applied to determine statistical significance, p = 0.015 and 0.004 for c-Cbl and c-Cbl-70Z (70Z) compared with control. Error bars = S.E. Inset, cell lysates of PAECs were probed using β-catenin, HA tag, and actin antibodies. Densitometry was performed to quantitate β-catenin normalized to actin using ImageJ. Representative immunoblot of three experiments is shown. B, endogenous c-Cbl/β-catenin interaction is enhanced with Wnt activation, and c-Cbl binds stronger to nuclear β-catenin in the Wnt-on phase. Immunoprecipitations (IPs) were performed with 500 μg of EC lysates from ECs pretreated with vehicle (Veh), Wnt3a (50 ng/ml), and Wnt3a with DKK1 (250 ng/ml) for 4 h using 1 μg of either rabbit polyclonal c-Cbl or rabbit preimmune serum (Ctr). The co-IPed β-catenin was detected using monoclonal β-catenin antibody. β-Catenin was IPed as described above using monoclonal β-catenin antibody or isotype control (Ctr). The co-IPed c-Cbl was detected using polyclonal c-Cbl antibody. Ten percent of cell lysates are shown as input and normalized to actin (data not shown) using ImageJ. The co-IPed β-catenin and c-Cbl were normalized to the immunoglobulin. Representative immunoblot of three experiments is shown. C, schematic of β-catenin constructs. β-Catenin constructs have an N-terminal Myc tag and include β-catenin wild-type (WT), S33A naturally occurring point mutation (S33A), N-terminal deletion (delN), C-terminal deletion (delC), and deletions of both the C and N termini with only the ARM region (ARM). D, c-Cbl binds to β-catenin ARM. HEK293T cells stably expressing HA tag c-Cbl were transiently transfected with Myc tag β-catenin constructs, and digitonin-extracted cytosolic fractions (5) were used for IP using HA and Myc antibodies, and co-IPed Myc-β-catenin or HA-c-Cbl was detected. Five percent of cell lysates are shown as input. Representative immunoblot from two experiments is shown. E, HA-tagged c-Cbl colocalizes with Myc-tagged β-catenin. HEK293T cells stably expressing HA-tagged c-Cbl and transiently expressing Myc-tagged β-catenin constructs were fixed and stained with polyclonal HA tag and monoclonal Myc tag antibodies. The scatter plots for colocalization were generated using the ImageJ program (National Institutes of Health) in cells having comparable signal levels for both constructs (5). Scatter plot points along the x or y axes represent absence of colocalization, whereas scatter plot points along a diagonal represent evidence of colocalization. F, schematic of c-Cbl constructs. TKB = tyrosine kinase binding domain; Linker region spans between tyrosine kinase binding and the RING finger domain, where the latter possesses E3 ligase activity; UBA = ubiquitin binding domain. c-Cbl-70Z construct lacks 17 amino acids from the linker domain and a part of RING domain. G, Wnt signaling enhances c-Cbl/β-catenin interaction and c-Cbl binds stronger to the nuclear active β-catenin in the Wnt-on phase. Purified recombinant GST-tagged c-Cbl(359–909) bound to glutathione-SepharoseTM beads was incubated with 500 μg of EC lysates pretreated with vehicle or Wnt-3a 50 ng/ml for 3 h prior to harvest. The eluent was immunoblotted using total β-catenin and active β-catenin antibodies. Five percent of cell lysates or GST-tagged c-Cbl are shown as input. GST-tagged proteins are shown as an input using Coomassie stain. Representative immunoblot from two experiments is shown. H, bacterially purified recombinant GST-tagged c-Cbl interacts with GST-tagged β-catenin in vitro. Purified recombinant GST-β-catenin was cleaved using thrombin, and the supernatant was treated with the purified recombinant GST or GST-tagged c-Cbl(359–909) bound to glutathione-SepharoseTM beads for 4 h. The beads were washed with buffer containing 0.25 m sodium chloride, and eluent was immunoblotted with β-catenin antibody. GST-tagged proteins are shown as an input using Coomassie stain. Representative immunoblot are of two experiments. WB, Western blot.