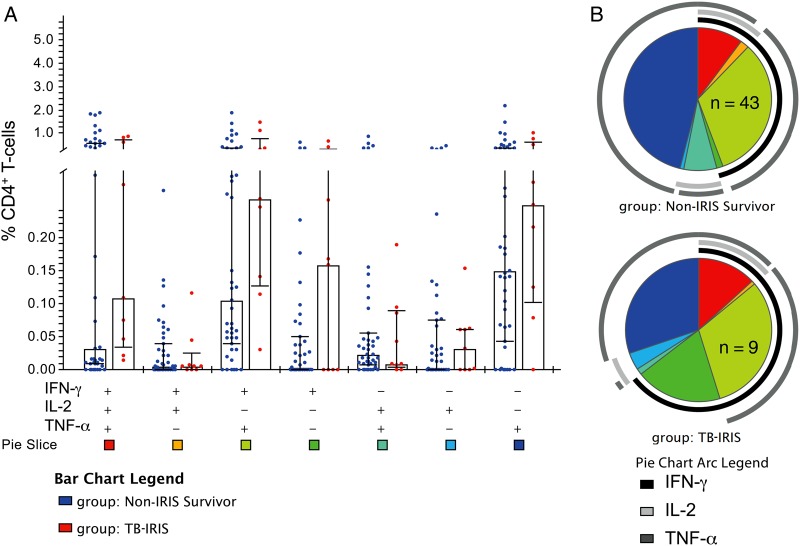
Figure 1.
Patients with tuberculosis-associated immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (TB-IRIS) tended to have elevated levels of TB-specific CD4+ T-cells expressing multiple cytokines prior to antiretroviral therapy (ART) initiation. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients obtained prior to ART initiation were stimulated with purified protein derivative (PPD) to measure TB-specific responses followed by intracellular cytokine staining and flow cytometry. Frequencies of TB-specific CD4+ T-cells expressing interferon gamma (IFN-γ), interleukin 2 (IL-2), and/or tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) at baseline in controls (n = 43) vs TB-IRIS patients (n = 9) were compared. A, Bar graph shows median frequency and interquartile range of the 7 possible combinations of IFN-γ, IL-2, and TNF-α expression by CD4+ T-cells in response to PPD stimulation in controls and TB-IRIS patients. B, Pie charts show the contribution of each combination of cytokine response to the total TB-specific responses mediated by CD4+ T-cells in controls and TB-IRIS patients. Colors in the pie charts correspond to the bottom of the bar graph, with pie arcs indicating the contribution of IFN-γ, IL-2, and TNF-α to the 3+ (poly), 2+, and 1+ (mono)-functional responses in non-IRIS survivors (controls) and TB-IRIS patients. Data shown are following subtraction of corresponding background responses. P values were >.05 for all comparisons shown in A and B by Wilcoxon rank-sum tests.