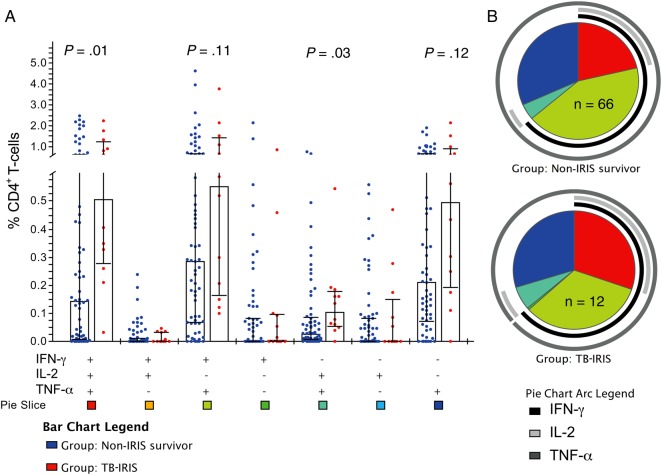
Figure 3.
After 4 weeks of antiretroviral therapy (ART), patients with tuberculosis-associated immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (TB-IRIS) have increased TB-specific production of multiple cytokines by CD4+ T-cells compared to controls. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients obtained at 4 weeks following ART initiation were stimulated with purified protein derivative to measure TB-specific responses. Cells were stained to quantitate cytokine responses by flow cytometry. The frequency of TB-specific CD4+ T-cells expressing interferon gamma (IFN-γ), interleukin 2 (IL-2), and/or tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) at week 4 post-ART in controls (n = 66) vs TB-IRIS patients (n = 12) is shown. A, Bar graph shows median frequency and interquartile range of the 7 possible combinations of TB-specific IFN-γ, IL-2, and TNF-α–expressing CD4+ T-cells in controls and TB-IRIS patients. B, Pie charts show the contribution of each combination of cytokine responses to the total TB-specific responses meditated by CD4+ T-cells in controls and TB-IRIS patients. Colors in the pie chart correspond to the pie slice colors shown at the bottom of the bar graph, with pie arcs indicating the contribution of IFN-γ, IL-2, and TNF-α to the 3+ (poly), 2+, and 1+ (mono)-functional responses in non-IRIS survivors (controls) and TB-IRIS patients. Data shown are following subtraction of corresponding background responses. Wilcoxon rank-sum tests were used to determine P values.