Fig. 4.
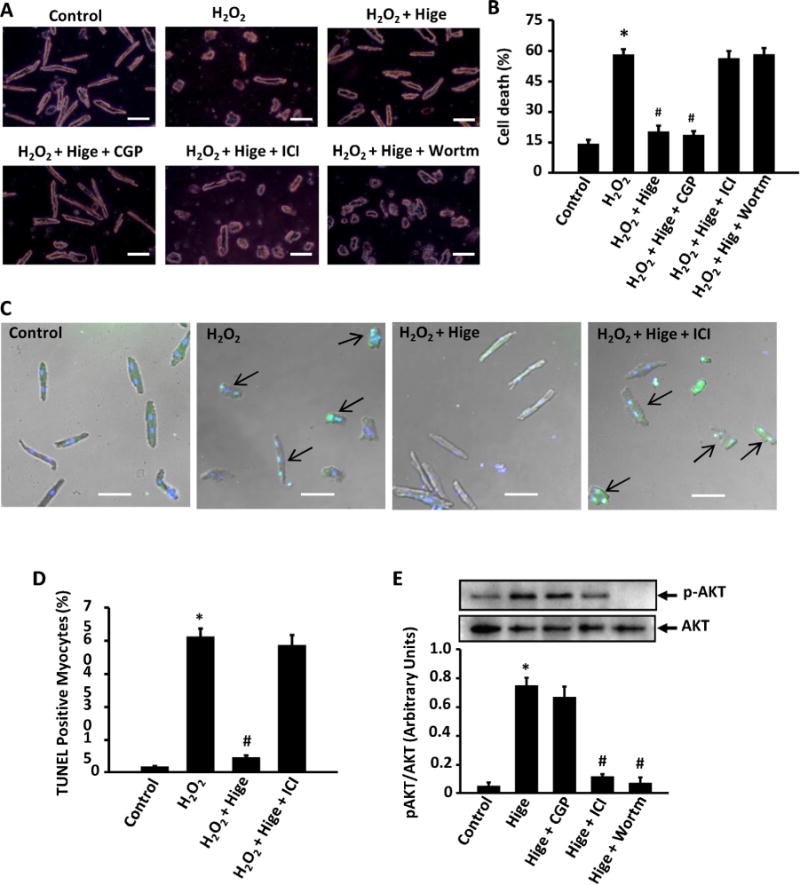
Role of β2-AR/PI3K/AKT pathway in higenamine mediated inhibition of H2O2-induced cell death, apoptosis, and AKT activation in AMVMs. (A) Trypan blue staining showing that the protective effect of Hignamine (100 μM) on H2O2 (20 μM for 24 h) induced cell death in adult mouse ventricular myocytes (AMVMs) were blocked by β2-AR specific inhibitor ICI118551 (0.5 μM) and PI3K inhibitor Wortmannin (10 μM), but not by β1-AR specific inhibitor CGP20712a (1 μM). Scale bar, 20 μm. (B) Quantification of A; (C) TUNEL staining of AMVMs showing that the anti-apoptotic effect of Higenamine (100 μM) on H2O2 (20 μM for 24 h) induced apoptosis was blocked by β2-AR specific inhibitor ICI118551 (0.5 μM). Scale bar, 20 μm. (D) Quantification of C. (E) The increase of AKT phosphorylation (activation) induced by Higenamine was attenuated by β2-AR specific inhibitor ICI118551 (0.5 μM) but not β1-AR specific inhibitor CGP20712a (1 μM). *P<0.05 vs. control cells, #P<0.05 vs. H2O2 treated cells, All results based on 3 independent duplicated experiments. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article).
