Figure 1.
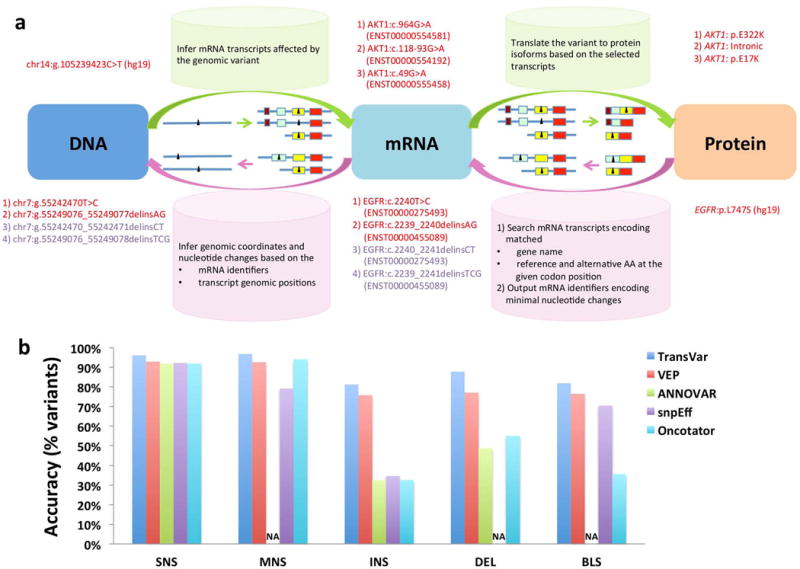
Schematic overview of TransVar and comparison of TransVar with other tools. (a) TransVar performs forward (green arrows) and reverse annotation (pink arrows) and considers all possible mRNA transcripts or protein isoforms available in user-specified reference genome and transcript databases (colored boxes representing exons in various transcripts or isoforms of a gene). Given a variant (black triangle) at any of the genomic, mRNA or protein levels, TransVar is able to infer the associated variants at the other two levels. In reverse annotation, TransVar searches all potential transcripts and reports one variant on each transcript. When there are multiple variants on the same transcript, TransVar reports the variant with minimal nucleotide changes (red text) instead of other alternatives (purple text). (b) Comparison of forward annotation consistency among TransVar, VEP, ANNOVAR, snpEff and Oncotator. Plotted are percentages of variants (Y axis) that had matched protein annotations in COSMIC v67 based on 964,132 unique SNSs, 3,715 MNSs, 11,761 INSs, 24,595 DELs and 166 BLSs (X axis). NA: Protein level annotations not available.
