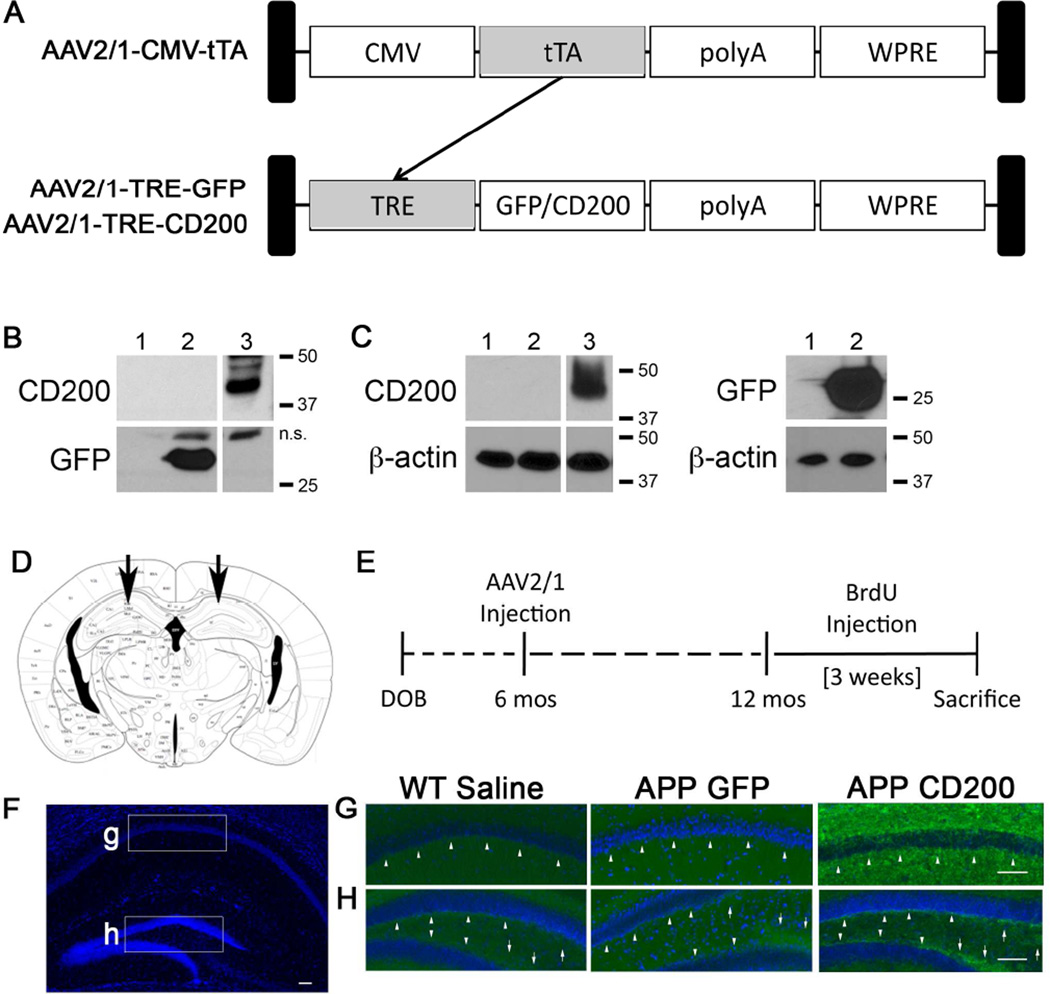
Figure 2. AAV2/1-TRE-CD200/AAV2/1-CMV-tTA-co-administration induces CD200 expression in vitro and in vivo.
(A) Schematic for our AAV2/1-CMV-tTA (tetracycline transactivor) and AAV2/1-TRE (tetracycline response element)-GFP/CD200 gene induction system. tTA gene expression under the CMV promoter induces expression of genes of interest (GFP or CD200) under the control of TRE and can be controlled by doxycycline (Tet-off system). (B, C) Each column has been given the following code: 1) Uninfected, 2) AAV2/1-TRE-GFP (1×109 VP/ml), and 3) AAV2/1-TRE-CD200FL (4×108 VP/ml)-infected samples. AAV293 cells (1×105 cells, B) and Primary murine cortical neurons (1×105 cells, C) were lysed 14 days after virus infection by RIPA buffer for immunoblot for CD200, GFP and β-actin. n.s: nonspecific bands. (D) The scheme depicts the location of the bilateral stereotactic injection into the CA1 region of the hippocampus in vivo (E) Experimental paradigm for in vivo study of AAV-injection into APP mice. (F–H) Hippocampal images taken from 12 month-old WT or APP mice injected with saline, AAV2/1-GFP or AAV2/1-CD200 at six months of age. Fixed brain tissue sections were immunostained for CD200 (green) and counter-stained with Hoechst 33342 (blue). Mice injected with AAV2/1-CD200 show increased intensity of CD200 staining in pyramidal neurons in the stratum radiatum of the CA1 (arrowheads) (G) and in the SGZ (arrowheads) and infrapyramidal and suprapyramidal mossy fiber neurons (arrows) of the DG (H). Scale bars represent 100 µm.