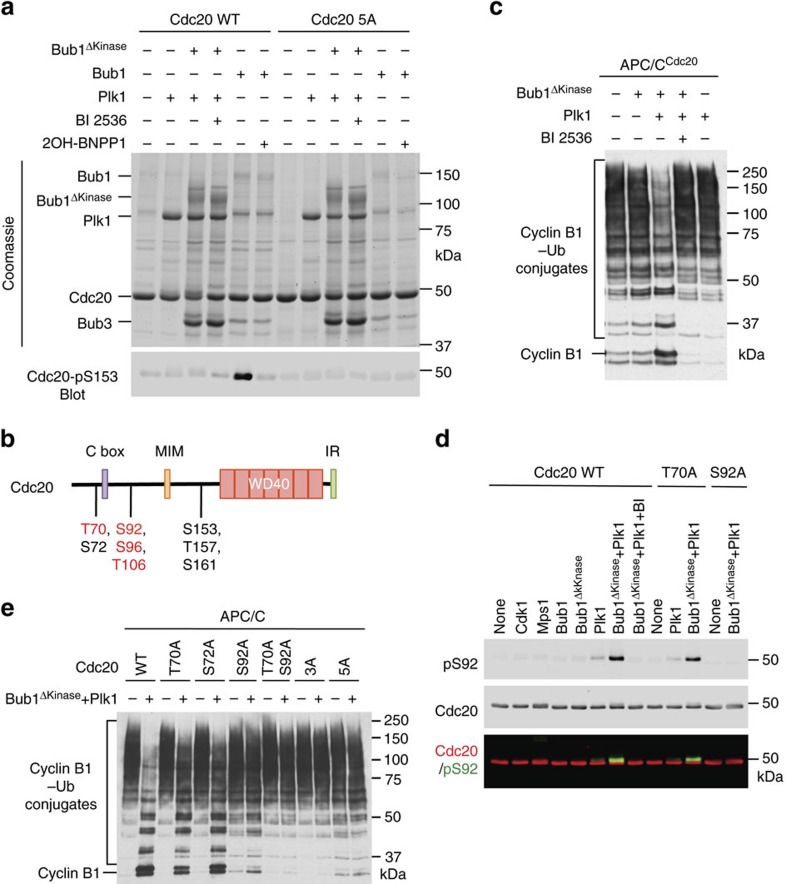
Figure 2. Bub1 promotes Plk1-mediated Cdc20 phosphorylation and APC/C inhibition.
(a) Coomassie-stained gel (top) and Cdc20-pS153 blot (bottom) of kinase reactions containing the indicated recombinant proteins and inhibitors. Cdc20 5A, S72A/S92A/S153A/T157A/S161A. (b) Domains and motifs of human Cdc20 with the important phosphorylation sites indicated. Sites in Bub1–Plk1-treated Cdc20 identified by mass spectrometry in this study are labelled in red. IR, isoleucine–arginine tail; MIM, Mad2-interacting motif. (c) Anti-Myc blot of the in-vitro ubiquitination reactions of APC/CCdc20 using cyclin B11–97–Myc as the substrate. Cdc20 was first incubated with the kinase buffer in the presence or absence of indicated proteins and BI 2536 before being added to APC/C isolated from Xenopus egg extract. (d) Quantitative immunoblots of the kinase reactions containing the indicated recombinant kinases and Cdc20 proteins as substrates. BI 2536 (BI) was added to one of these reactions. The Cdc20-pS92 and total Cdc20 signals on the same membrane were detected in the 800- and 700-nm channels, respectively. The two channels were pseudo-coloured (Cdc20-pS92, green and Cdc20, red) and overlaid in the bottom panel. (e) Anti-Myc blot of the in-vitro ubiquitination reactions of APC/CCdc20 using cyclin B11–97–Myc as the substrate. The indicated Cdc20 proteins were first incubated with the kinase buffer in the presence and absence of Bub1ΔKinase and Plk1, and then added to APC/C isolated from Xenopus egg extracts. Cdc20 3A, T70A/S72A/S92A.