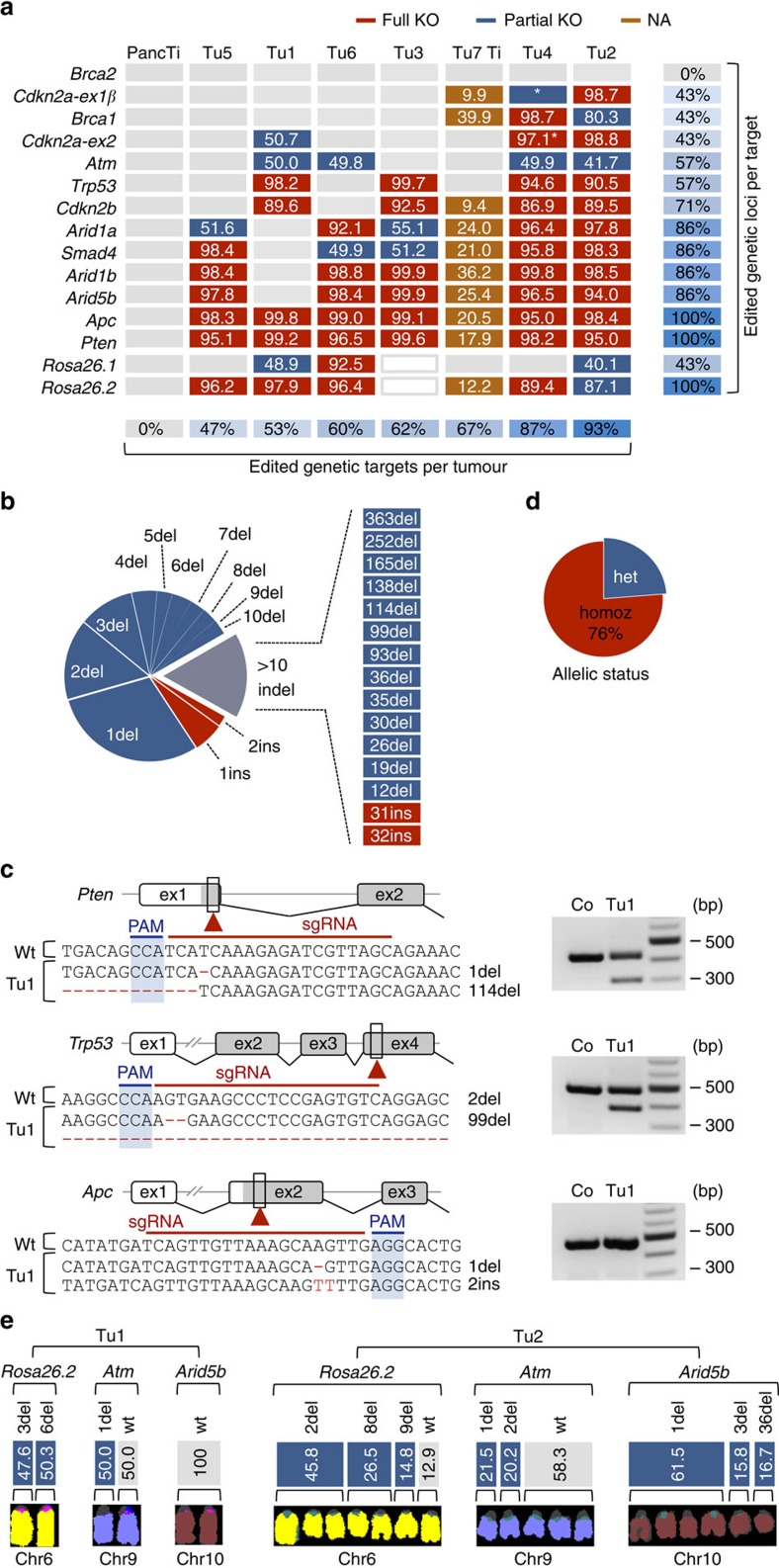
Figure 4. Target site mutations in CRISPR/Cas-induced cancers.
(a) Indels and allelic status at each target site in electroporated healthy pancreatic tissue (PancTi), PDAC cell lines (Tu1-6) and primary tumour tissue (Tu7 Ti). Numbers in boxes indicate for each target site mutant read frequencies (MRFs; defined as the fraction of mutant sequence reads/all reads at individual target loci). Multiple mutations per target site are presented as one combined MRF. A more detailed presentation of the different mutations at individual target sites is shown in Supplementary Fig. 2. Red and blue boxes indicate complete or partial inactivation of targeted loci, respectively. A target locus was defined to be only partially inactivated if at least one chromosome with non-mutated wild-type sequence was retained. For tissue (brown boxes), assumptions about full/partial inactivation cannot be made. Grey boxes designate a lack of mutations at target sites. The asterisk stands for a large deletion at the Cdkn2a locus with fusion of Cdkn2a-ex1β and Cdkn2a-ex2 (see also Fig. 6). White boxes (Tu3) indicate electroporation without Rosa26.1 and Rosa26.2 control guides. (b) Spectrum and distribution of indel types and sizes in all sequenced tumours. Del, deletion; Ins, insertion. (c) Examples and sequence context of CRISPR/Cas9-induced homozygous (homoz) mutations at target sites. Large deletions were also detectable by PCR, showing additional shortened products. PAM, protospacer adjacent motive; ex, exon and Co, control. (d) Allelic status at target sites across tumours. Homozygousity was defined by a lack of wild-type sequence reads in cancer cell cultures. Het, heterozygous. (e) Examples of mutational spectra in a diploid (Tu1) and a poly-/aneuploidy cancer (Tu2). M-FISH and target site sequencing were performed on the cell lines. Results are shown for three representative target genes. MRFs of target site mutations are assigned to individual chromosomes. The existence of more than two mutations at a target site in Tu2 reflects early polyploidization during transient CRISPR/Cas9 expression. Comprehensive data for all chromosomes are shown in Supplementary Fig. 4.