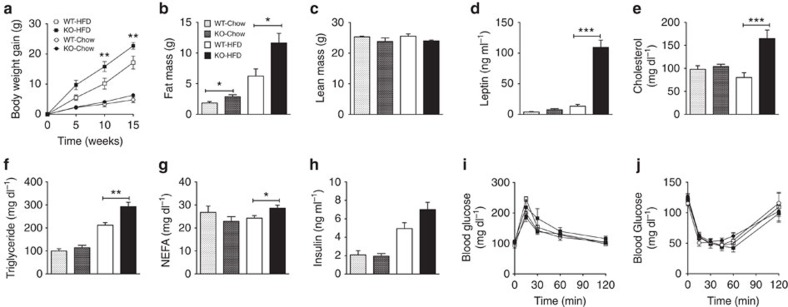
Figure 2. HDAC5 knock-out mice are prone to diet-induced obesity.
Male HDAC5 WT and KO littermates were subjected to either chow or HFD and evaluated for (a) body weight gain over a total of 15 weeks; (b) fat and (c) lean mass after 8 weeks of chow or HFD exposure (n=6–8). After 10 weeks of HFD and 15 weeks of chow exposure, plasma (d) leptin, (e) cholesterol, (f) triglyceride, (g) non-esterified fatty acid and (h) insulin levels were measured in additional cohorts of chow- or HFD-fed HDAC5 WT (n=6–7) and KO mice (n=9–10). (i) Glucose tolerance and (j) insulin tolerance tests were carried out after 8 weeks of diet exposure (n=4–8). Values represent means±s.e.m. Statistical analyses were done by either two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc tests (a,i,j), or two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test (b–h). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001.