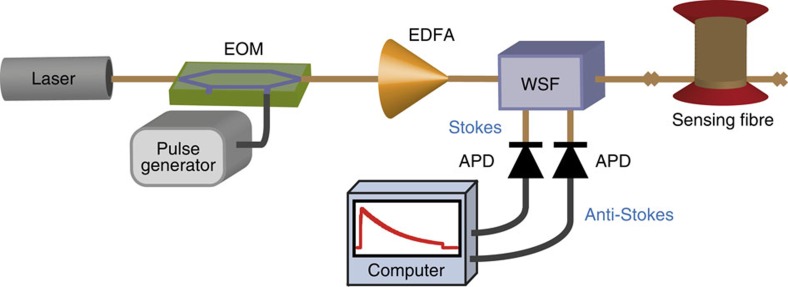
Figure 6. Experimental setup of a basic Raman-distributed sensor.
The system operates using a conventional distributed-feedback laser operating at 1,552 nm, followed by an electro-optic modulator (EOM) to generate pulses of 10 ns and an erbium-doped fibre amplifier (EDFA) to boost the pulse power. Optical pulses of about 4W peak power are launched into the sensing fibre through a wavelength-selective filter (WSF), which also separates the spontaneous Stokes and anti-Stokes Raman components backscattered from the sensing fibre into two branches. These two spectral components are sent into two parallel 50 MHz avalanche photodetectors (APD), followed by an acquisition system connected to a computer. The sensing fibre corresponds to a 50/125-μm graded-index multimode fibre 9 km long. As a result of intermodal dispersion, the spatial resolution at the end of the sensing fibre is ∼2 m.