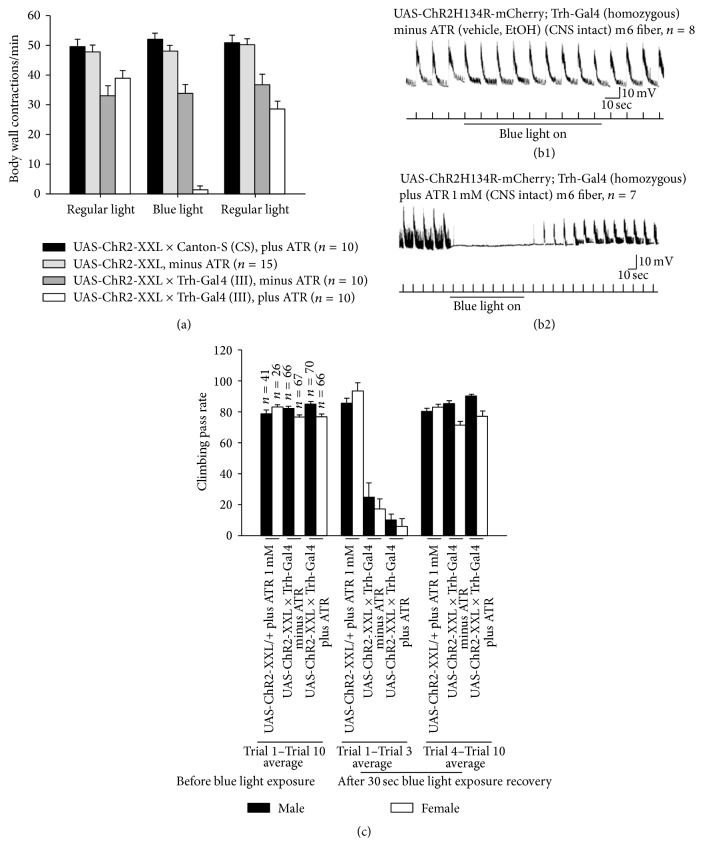
Figure 16.
Serotonergic neuron activation modulates locomotor behavior in third-instar larvae and adult flies. (a) To change serotonergic neuron activity, ChR2 was expressed in serotonergic neurons (UAS-ChR2-XXL/+; Trh-Gal4/+). The body wall contractions were counted in third-instar larvae fed on food supplemented with ATR 1 mM or ethanol (vehicle). When the larvae, which were fed on ATR 1 mM, were exposed to blue light, the locomotor activity was significantly compromised. However, when the larvae fed on a food without ATR (b1) supplementation were exposed to blue light, the locomotor activity was not significantly affected. Fly food not supplemented with ATR and exposed to blue light did not suppress sensorimotor activity in dissected third-instar larvae; however, (b2) serotonergic neuron activation by exposing the third-instar larvae, which were fed food supplemented with ATR (1 mM), to blue light shut down sensory-motor circuit activity. The sensory-motor circuit was being activated by trains of stimulations at 40 Hz, 10 pulses, while the motor output was being recorded in abdominal muscle 6 (m6). (c) Climbing assay in adult flies was used to test the locomotive ability of the flies. Activation of serotonergic neurons in adult flies decreases climbing ability. The excitability of serotonergic neurons is increased by expressing and activating ChR2 by blue light. When the adult flies were being exposed to blue light, the climbing ability significantly reduced. Both flies groups (UAS-ChR2-XXL/+; Trh-Gal4/+) which were fed food supplemented with ATR 1 mM or ethanol (vehicle) were affected by the blue light exposure. However, blue light did not have effect on the control lines (UAS-ChR2-XXL × Canton-S, shown as UAS-ChR2-XXL/+). The climbing assay was repeated 10 times and the average (Trial 1–Trial 10 average) was taken. There was a 1 min rest interval between two trials before blue light exposure. Moreover, after exposing the flies to blue light for 30 sec, the climbing assay was repeated for 10 trials. The average was taken for Trial 1–Trial 3 since the locomotion activity was decreased during this period. The average was taken for Trial 4–Trial 10, in which the flies started recovering after blue light exposure.