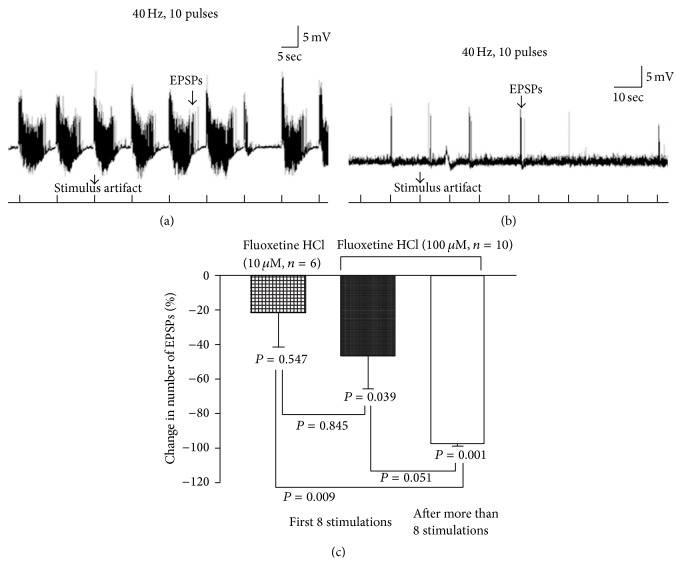
Figure 17.
Motor-sensory function and action of a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI). (a) Evoked sensory-motor neural activity (EPSPs) was recorded from body wall muscle fiber 6 or 7 of third-instar larvae in saline. (b) Application of fluoxetine (100 μM) suppresses the evoked activity of the neural circuitry. (c) Fluoxetine at 10 μM did not significantly decrease activity but there is a decreasing trend in the mean change in the sensory-motor function. Paired t-test was used to compare the frequency of EPSPs inside saline and fluoxetine. One-way ANOVA was used to compare different treatments. Bonferroni t-test was employed to obtain significant results. Data represented as mean ± SEM. P < 0.05 is significant.