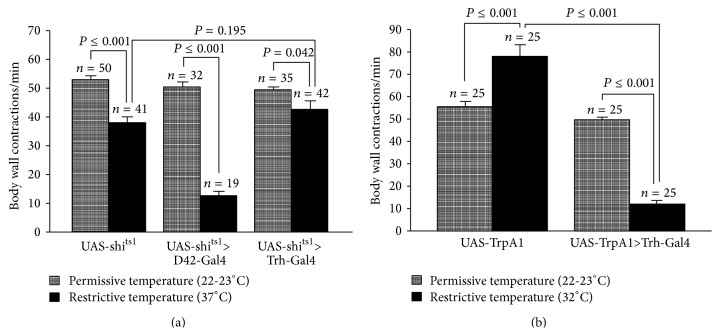
Figure 9.
Acute manipulation of 5-HTergic neurons activity by shi ts1 and TrpA1. (a) Synaptic transmission was blocked in the 5-HTergic neurons by expressing dominant negative temperature sensitive shibire ts1 allele (shi ts1). Suppression of synaptic transmission in motor neurons (UAS-shi ts1>D42-Gal4) significantly reduced body wall contractions; however, suppression of synaptic transmission in 5-HT neurons (UAS-shi ts1>Trh-Gal4 (III)) did not significantly influence body wall contractions. The flies were raised at 23°C, 12 : 12 LD cycle. To obtain the locomotion behavior at room temperature for control and shibire ts1 expressing larvae, an individual third-instar larva was placed on the apple-juice agar. The larva was left for 1 min to acclimate, and body wall contractions were counted for the following 1 min. To obtain body wall contractions at restrictive temperature for control and shibire ts1 expressing larvae, the larvae were incubated at 37°C for 20 min. The individual larvae were placed on prewarmed apple-juice agar on hot plate (30–32°C). The larva was left for 1 min to acclimate, and the body wall contractions were counted for the following 1 min. (b) Thermogenetic approach was used to activate 5-HTergic neurons. When TrpA1 channels are exposed to high temperature (32°C), they become activated which leads to inward current flux of cations. Activation of 5-HTergic neurons (UAS-TrpA1>Trh-Gal4 (III)) significantly decreases BWCs compared to control larvae (UAS-TrpA1). To obtain BWCs at room temperature, larvae were placed on apple-juice agar dish at room temperature and left for 2 min to acclimate. Afterwards, BWCs were counted for 1 min. The locomotor behavior at restrictive temperature (32°C) was obtained by placing one larva on a prewarmed apple-juice agar dish on a hot plate (32°C). The larvae were left for 2 min, and then the BWCs were counted for 1 min. Student's t-test was performed to carry out comparison between groups. Data presented as mean ± SEM. P < 0.05 is significant.