Figure 6.
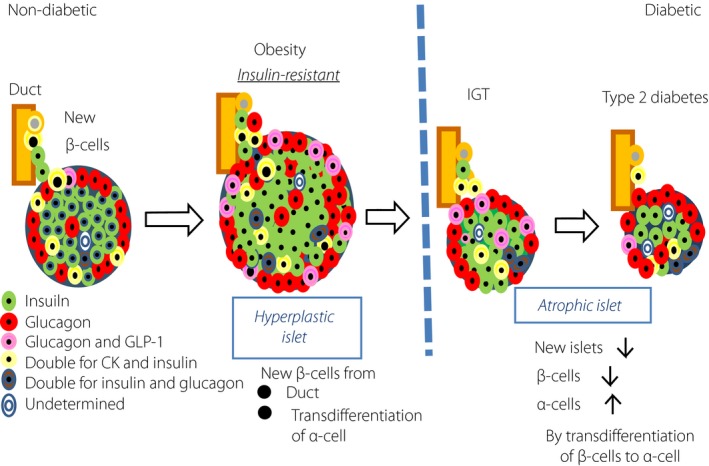
Emerging concept of islet endocrine cell transdifferentiation (metaplasia)50. There is remodeling of islet endocrine cells in obese or diabetic subjects. In healthy control subjects, islet β‐cells undergo compensatory hyperplastic changes in response to obesity. For this background, it is proposed that increased β‐cells derive from α‐cells by transdifferentiation in obese insulin‐resistant subjects. In contrast, with continuing metabolic stress, transcription factor FOXO1 is suppressed to translocate to nuclei, resulting in promoting transdifferentiation of α‐cells to β‐cells48. Such transdifferentiation of β‐cells to α‐cells are supposed to contribute to decreased β‐cell volume density in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) and type 2 diabetes49. CK, cytokeratin; GLP‐1, glucagon‐like peptide‐1.
