Figure 8.
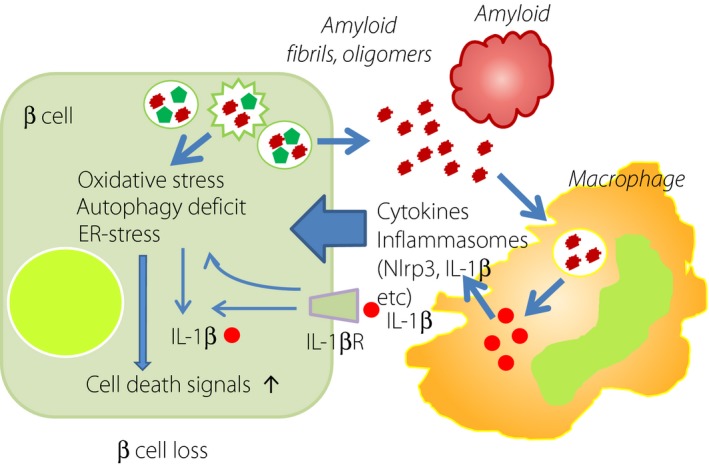
Pro‐inflammatory activation and amyloid deposition in the islet of type 2 diabetes. In the islet of type 2 diabetes, there is an increase in macrophage infiltration particular to pro‐inflammatory type 1. Amyloid deposition accelerates macrophage migration, and the release of cytokines and inflammasomes, such as Nlrp3 and interleukin‐1β (IL‐1β). IL‐1β in turn elicits β‐cell injury to disturb insulin secretion. Amyloid fibrils and oligomers are toxic to β‐cells, and augment the cell death pathway through oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress or autophagy deficits. IL‐1βR, interleukin‐1β receptor.
