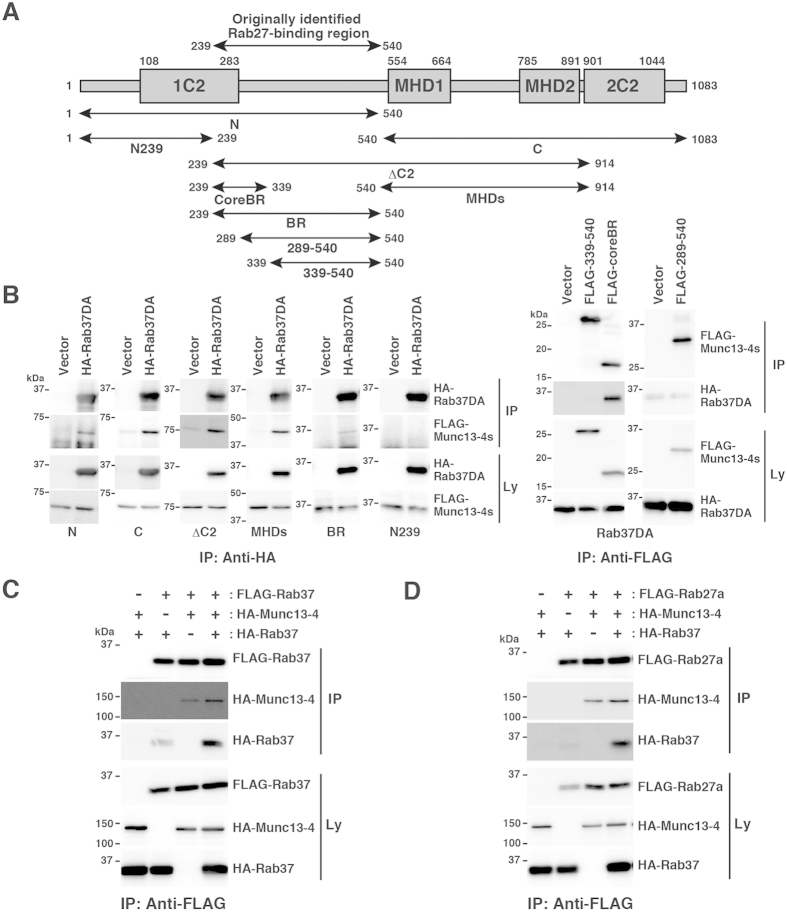
Figure 6. Analysis of the Rab37-Munc13-4 interaction.
(A) Schematic representation of mutant Munc13-4 constructs. Domain organisation of Munc13-4 and amino acid positions corresponding to the truncation boundaries of each construct are shown. 1C2: the first Ca2+ -binding C2 domain, 2C2: the second Ca2+ -binding C2 domain, MHD1: the first Munc13 homology domain, and MHD2: the second Munc13 homology domain. (B) Identification of Rab37-interacting regions in Munc13-4 protein. Lysates from COS7 cells transfected with HA-Rab37DA or control (Vector) plasmid, together with the expression plasmid for FLAG-tagged Munc13-4 mutant protein presented in (A) were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-HA or anti-FLAG antibody as indicated. The lysates (Ly) and immunoprecipitates (IP) were subjected to western blot analyses with anti-HA (3F10) or anti-FLAG antibody. (C) Multiple Rab37 proteins interact with Munc13-4. COS7 cells were transfected with (+) or without (−) the following plasmids as indicated: FLAG-Rab37, HA-Munc13-4, and HA-Rab37 plasmids. The transfected cells were then lysed and subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG antibody. The lysates (Ly) and immunoprecipitates (IP) were then analysed as in (B). (D) Formation of a Rab27-Munc13-4-Rab37 complex. COS7 cells were transfected with (+) or without (−) the following plasmids as indicated: FLAG-Rab27a, HA-Munc13-4, and HA-Rab37 plasmids. The transfected cells were then lysed in the presence of GTPγS and subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-FLAG antibody. The lysates (Ly) and immunoprecipitates (IP) were then analysed as in (B). The full-length blotting images of (B−D) are presented in Supplementary Figs. S18, S20, and S21, respectively.