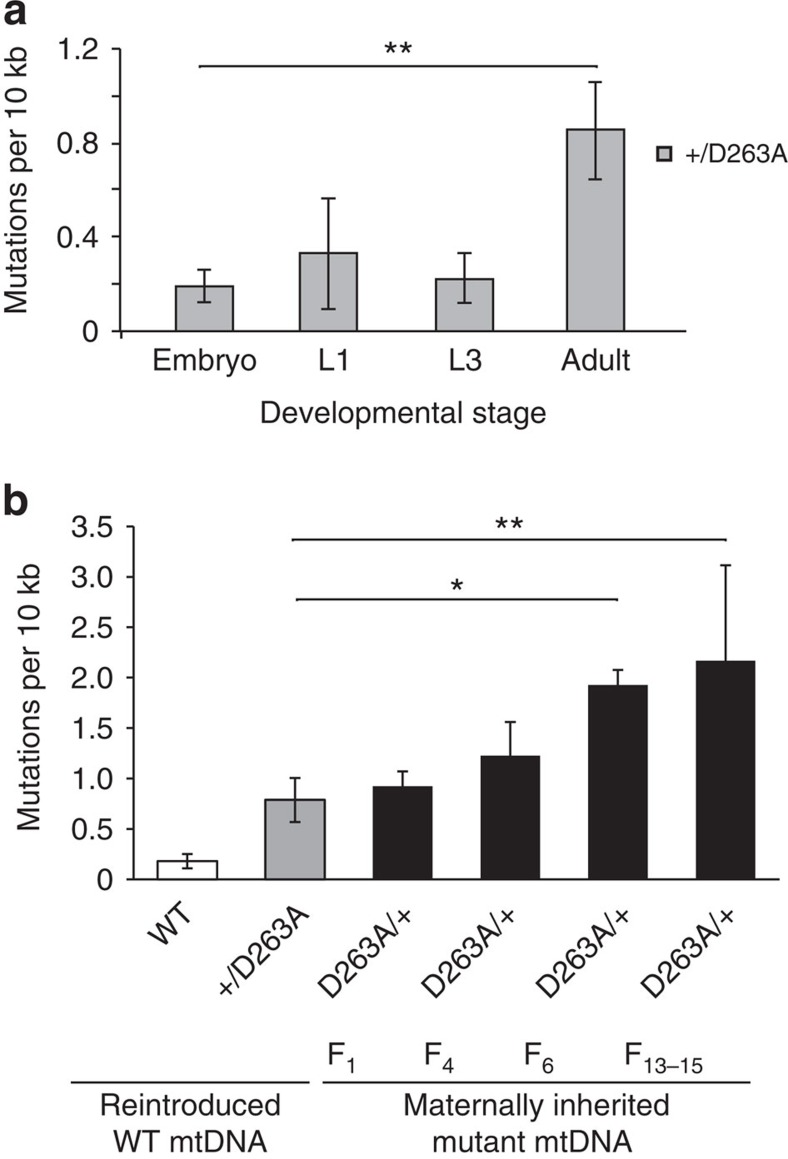
Figure 6. MtDNA mutations increase after morphogenesis and accumulate transgenerationally.
(a) MtDNA mutation load was determined in heterozygous D263A flies in different developmental stages. The D263A exo− allele was transmitted paternally and therefore all the detected mutations are produced by somatic mutagenesis. An increase in the mtDNA mutation load relative to wild-type (WT) flies was only detected after morphogenesis. One-way ANOVA with Dunnett's post hoc test. **P<0.01. Error bars represent s.d. n=3–6. (b) MtDNA mutations accumulated in heterozygous D263A exo− flies after successive intercrossing for several generations. MtDNA mutation loads were compared among wild-type flies (WT, white bar), heterozygous D263A exo− flies with a clean background (+/D263A, lack maternally transmitted mtDNA mutations, grey bar) and heterozygous D263A exo− flies that maternally inherited mtDNA mutations for 1, 4, 6 or 13–15 generations (D263A/+, black bar). One-way ANOVA with Dunnett's post hoc test. **P<0.01, *P<0.05. Error bars represent s.d. n=3–6.