Fig. 4.
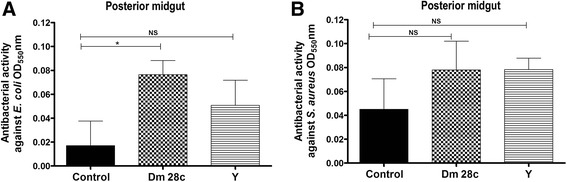
Antibacterial activity in the posterior midgut of Rhodnius prolixus infected with Trypanosoma cruzi. R. prolixus 5th instar nymphs were fed inactivated blood containing the T. cruzi Dm 28c clone or Y strain at a final concentration of 1 × 107 epimastigotes/mL. The antibacterial activities were measured in vitro in posterior midgut samples seven days after infection and tested against (a) E. coli and (b) S. aureus. Treatments: black columns-uninfected insects; grid columns-T. cruzi Dm 28c-infected insects; striped columns-T. cruzi Y-infected insects. Antibacterial activity was measured through optical densities using the turbidimetric assay (OD550 nm) after 19 h of incubation of posterior midgut samples with bacteria. Bars represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments with nine pools of insects (n = 9). Means were compared using one-way ANOVA and Student’s T-test; * p < 0.05
