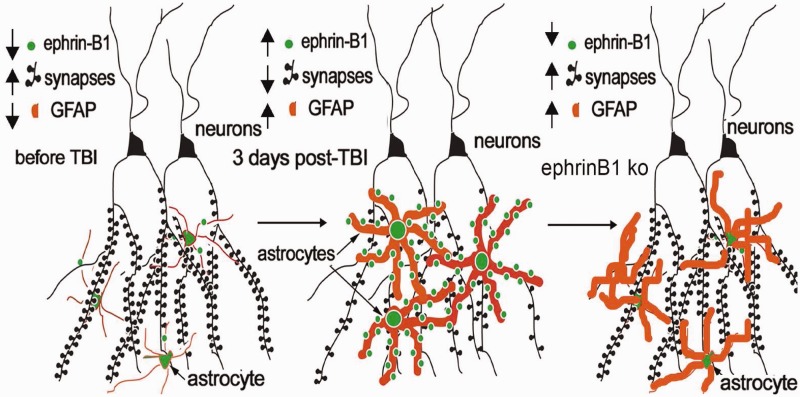
Figure 8.
Visual depiction of hypothesis. Increased ephrin-B1 immunoreactivity in astrocytes coincide with a reduction in vGlut1-positive glutamatergic innervation of CA1 hippocampal neurons in SR at 3 dpi (middle panel), suggesting that astrocytic ephrin-B1 may regulate synapse reorganization in the hippocampus following CCI. Astrocyte-specific deletion of ephrin-B1 accelerates recovery of vGlut1-positive glutamatergic innervation of CA1 hippocampal neurons in SR after CCI (right panel).