Figure 2.
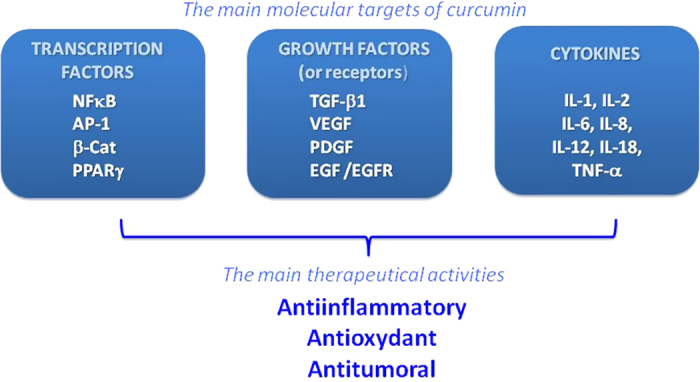
Main molecular targets regulated by curcumin involved in its therapeutical activities. Curcumin modulates (i) various transcription factors such as NF-κB (nuclear factor κB), AP-1 (activating protein-1), β-cat (β-catenin) and PPARγ (peroxisome proliferator-associated receptor gamma), (ii) growth factors including TGF-β1 (tumor growth factor -β1), VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor), PDGF (platelet-derived growth factor), EGF (epidermal growth factor) and its receptor EGFR and (iii) cytokines such as IL (interleukin) and TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor α). Regulation of these molecular targets contributes to its therapeutical interest as anti-inflammatory, antioxydant and anti-cancer agent.
