Fig. 3.
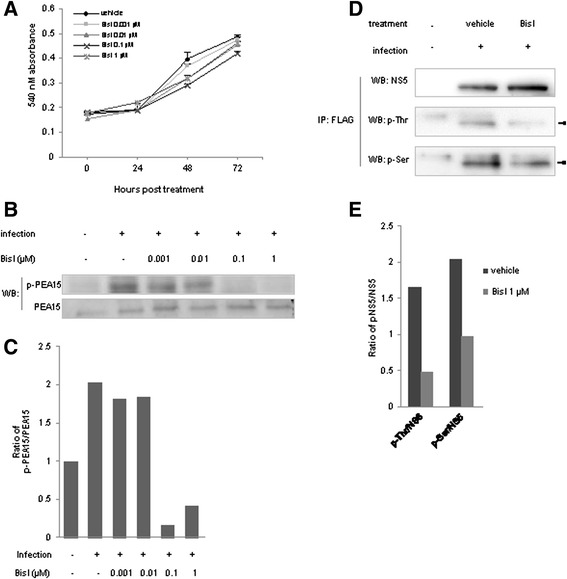
Inhibition of PKC by BisI. a Inhibition of PKC by BisI did not alter host cell growth. HepG2 cells were treated with various concentrations of BisI. Average cell viability from right after the treatment (0 h), 24, 48, and 72 h was monitored by MTT assays. Error bars represented S.D. from 3 independent experiments. b BisI effectively inhibited PKC activity. Phosphorylation of PEA15, a known substrate of PKC. Levels of phospho-PEA15 at 24 h after BisI treatment were examined by immunoblotting using a phospho-PEA15 (p-PEA15) specific antibody. Concentrations of BisI used were indicated. PEA15 immunoblot was used to examine the total amount of PEA15. c Quantification of p-PEA15 from b Amounts of p-PEA15 were normalized by total PEA15. d PKC inhibition by 1 μM of BisI downregulated NS5 Threonine and Serine phosphorylations. BHK-21 cells were infected with recombinant DENV expressing His-FLAG-NS5, and tagged protein was then pulled down by anti-FLAG antibody. The p-Thr and p-Ser were examined by immunobloting as in Fig. 2b. Arrow heads indicated specific p-Thr or p-Ser signals. e Quantifications of p-Thr/NS5 and p-Ser/NS5 from (d)
