Figure 4.
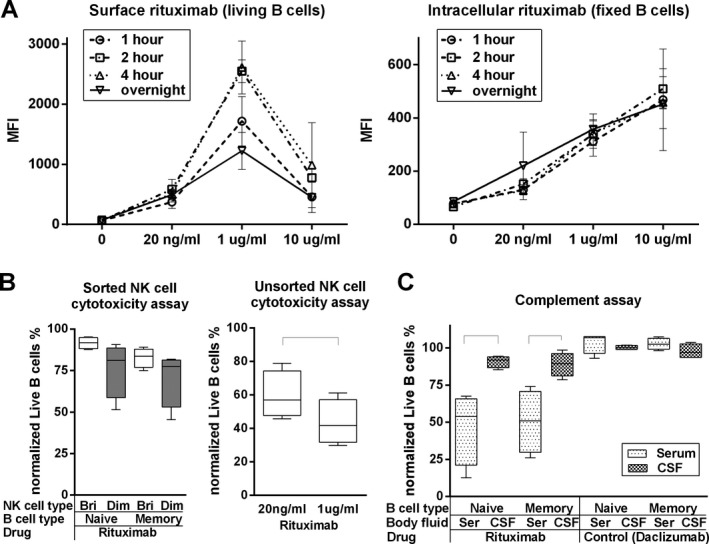
The low levels of complement components in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) underlies poor B‐cell depletion in the intrathecal compartment. (A) In vitro B‐cell surface and intracellular rituximab saturation assay. Purified B cells were cultured in the absence or presence of different concentrations of rituximab (10 μg/mL, 1 μg/mL [average serum concentration in current study], 20 ng/mL [average CSF concentration in current study], using time‐assay (1, 2, 4 h or overnight). Surface or intracellular rituximab mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of living or fixed B cells was measured by flow cytometry. Error bars represent standard deviation (SD). (B left) In vitro NK cell cytotoxicity assay. Sorted CD56dim or CD56bright NK cells and negatively purified naïve and memory B cells were obtained. Each NK cell type was seeded with equal number of either Naïve B cells or Memory B cells for 6 h, in the presence of 1 μg/mL of rituximab. Cytotoxicity of NK cells to B cells was calculated as: % cytotoxicity = (relative B cell numbers in the sample/relative B cell numbers in B cell control) × 100. (B right) In vitro rituximab dose‐dependent NK cell cytotoxicity assay. Negatively selected NK cells were cultured for 6 h with equal number of negatively selected B cells, in the presence of either 1 μg/mL or 20 ng/mL of rituximab. Cytotoxicity of NK cells to B cells was determined by the % cytotoxicity formula. Black brackets represent statistical significant (P < 0.05) difference between the two conditions based on the paired t‐test. (C) In vitro B cell cytotoxicity assay. Negatively purified naïve and memory B cells was cultured 4 h with rituximab (1 μg/mL) or a control antibody (daclizumab: 1 μg/mL) in the presence of 50% serum or pooled multiple sclerosis CSF samples (to assure identical conditions for all donors). Cytotoxicity of NK cells to B cells was determined by the % cytotoxicity formula. Black brackets represent statistical significant (P < 0.05) difference between the two conditions based on the paired t‐test.
