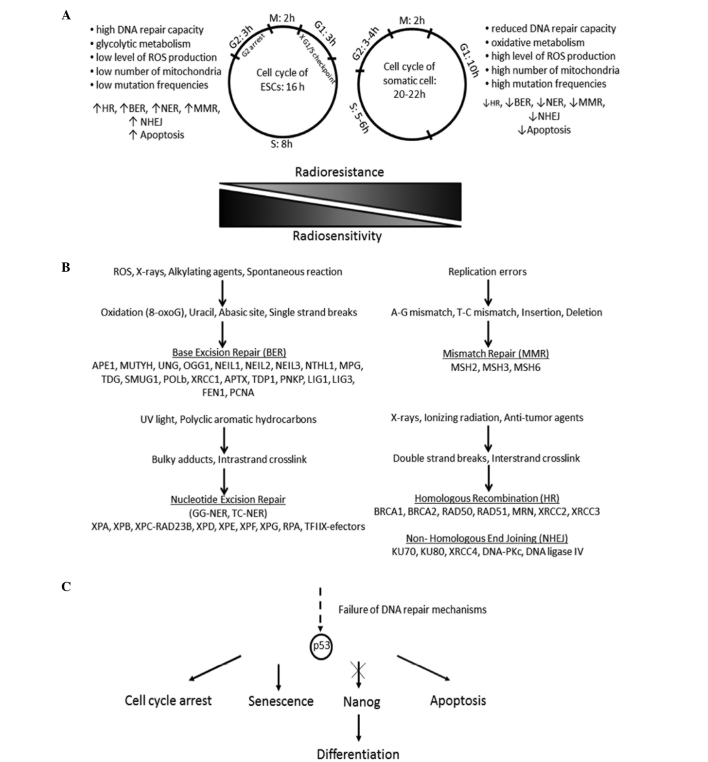
Figure 1.
(A) Response of undifferentiated and differentiated cells to genotoxic agents differs, because of distinct cell cycle and cell metabolism. (B) Mammalian cells are exposed to the influence of DNA damage (single- or double-strand breaks) agents. In DNA repair mechanisms, base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair (NER), mismatch repair, homologous recombination and non-homologous end joining are involved many genes. (C) Failure of DNA repair may direct the cells to apoptosis or to differentiation. ESCs, embryonic stem cells; ROS, reactive oxygen species; GG-NER, global genome-NER; TC-NER, transcription-coupled NER.