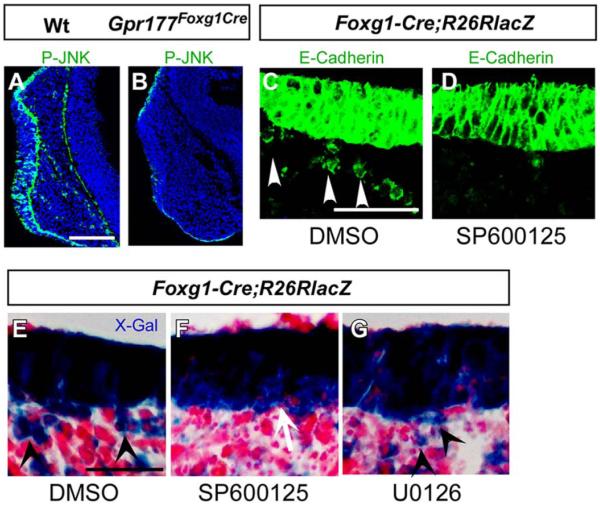
Fig. 6.
A Gpr177/JNK signaling is required for nasal epithelial cell migration. A,B: Immunofluorescent staining shows that phosphorylated JNK is reduced in the epithelium and completely abolished in the mesenchyme of Gpr177Foxg1-Cre embryos (B) comparing with the wild-type (A). C–G: Immunofluorescence and X-gal staining on the sections of R26RLacZFoxg1-Cre facial explants shows that the epithelial cell migration is inhibited with treatment of SP600125 (D, F vs. C, E). Note that the migrating cells with positive staining are present in dimethyl sulfoxide group (C,E) and U0126 (G), but not in SP600125 (D,F) group. Arrowheads indicate migrating epithelial cells. Scale bars ¼ 100 mm in A,B; 50 mm in C–G.