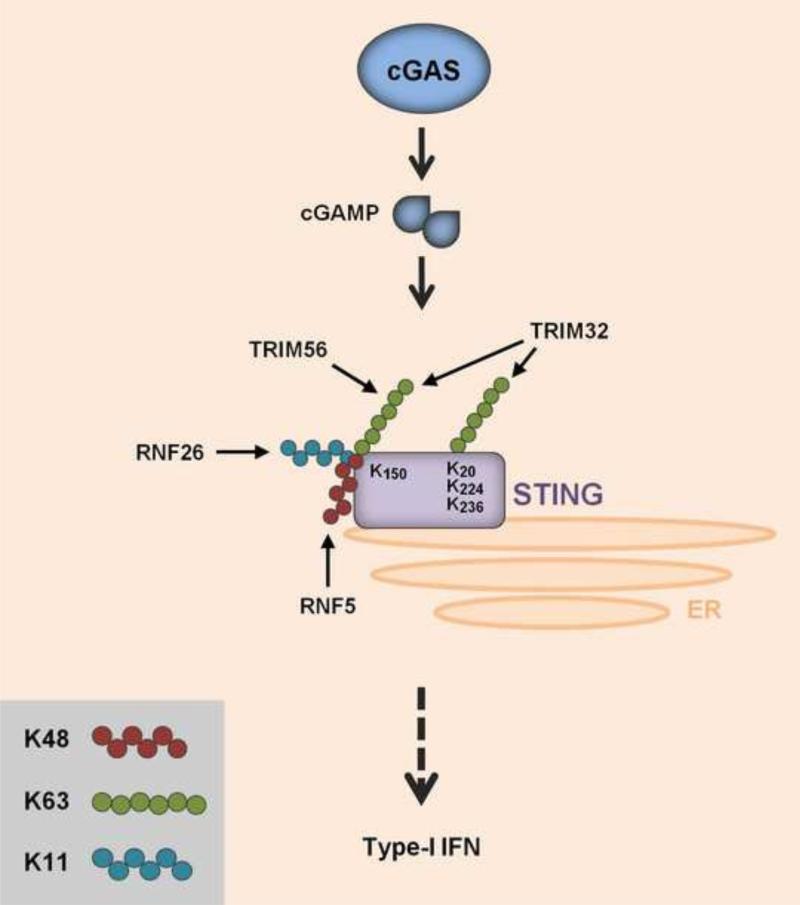
Figure 4. Regulation of the cGAS-STING pathway by ubiquitination.
cGAS recognizes viral DNA in the cytoplasm and synthesizes cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP). cGAMP then activates STING on the ER, inducing downstream signaling for type-I IFN induction. STING is regulated by three types of polyubiquitination: K11-linked and K63-linked ubiquitination of K150 by RNF26 and TRIM56 or TRIM32, respectively, facilitating STING activation and type-I IFN gene expression. Besides K500, TRIM32 ubiquitinates three other residues in STING (K20, K224 and K236). Furthermore, K500 in STING is covalently modified by K48-linked ubiquitination mediated by RNF5. RNF5-induced STING ubiquitination leads to STING degradation.