Fig. 3 -.
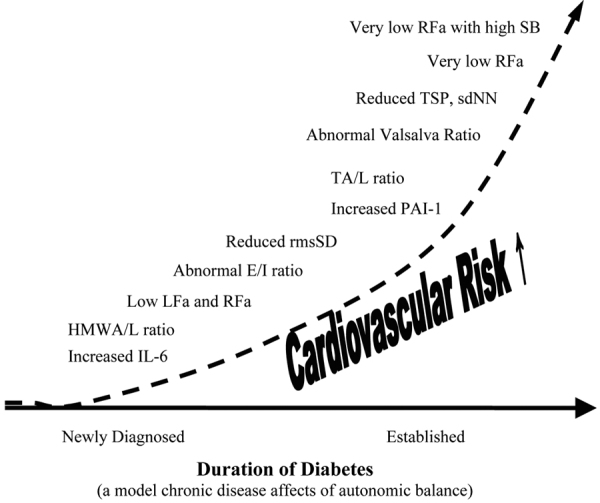
The natural history of autonomic balance, based on diabetes as a model of the affect of chronic disease on the autonomic nervous system. IL-6 = Interleukin-6, an inflammatory marker; HMWA/L = high-molecular weight adiponectin-to-leptin ratio, an inflammatory marker; LFa = low frequency area, a pure measure of sympathetic activity (based on concurrent spectral analyses of continuous measures of both respiratory activity and HRV); RFa = respiratory frequency area, a pure measure of parasympathetic activity (based on concurrent spectral analyses of continuous measures of both respiratory activity and HRV); E/I ratio = the ratio of the peak exhalation R-R interval to the peak inhalation R-R interval (R-R interval is the interval between two consecutive heart beats, and is a qualitative measure of more or less parasympathetic activity; rmsSD = root mean square of standard deviation, a statistical measure of heart rate variability (HRV), and is a qualitative measure of more or less parasympathetic activity; PAI-1 = plasminogen activator Inhibitor 1, an inflammatory marker; TA/L ratio = total adiponectin/leptin ratio, an inflammatory marker; Valsalva ratio = the ratio of the longest to shortest R-R interval during a 15 second Valsalva maneuver, a qualitative measure of more or less parasympathetic activity; TSP = total spectral power, a measure of gross autonomic activity (parasympathetic plus sympathetic activity); sdNN = standard deviation of the beat-to-beat (R-R) intervals, a measure of gross autonomic activity (parasympathetic plus sympathetic activity); RFa = respiratory frequency area, a pure measure of parasympathetic activity (based on concurrent spectral analyses of continuous measures of both respiratory activity and HRV); SB = Sympathovagal Balance = ratio of resting sympathetic activity to resting parasympathetic activity. Very low RFa is a definition of Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy (CAN), increased indicating mortality risk. CAN with high SB is associated with high mortality risk (see text) (24).
