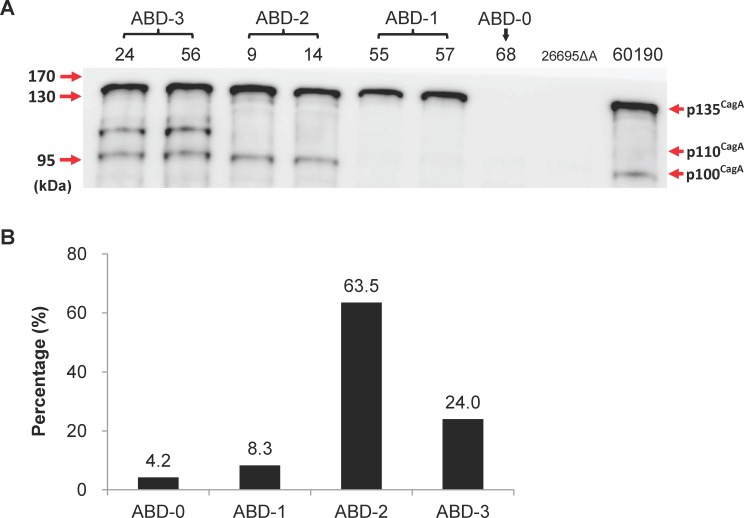
Fig 4. Analysis of the CagA protein patterns by immunoblot analysis.
(A) Lysates of H. pylori isolated from the tissue specimens of various gastric patients were prepared as described in the Materials and Methods. Aliquots of protein (20 μg) were separated by SDS-gel electrophoresis and CagA was detected by immunoblotting using polyclonal anti-CagA antibody b-300 (Santa Cruz). The H. pylori 60190 and 26695 cagA knockout mutant (26695ΔA) were included as a positive and negative control, respectively, for CagA expression. The numbers at the top identify the various H. pylori colonies, while those on the left indicate the molecular weight markers in kDa. It can be seen that there are four types of CagA fragmentation patterns. (B) The percentages of ABD subtypes based on the CagA protein fragmentation patterns across the 96 H. pylori cagA ABD colonies that were analyzed and clearly ABD-2 is the predominant type.