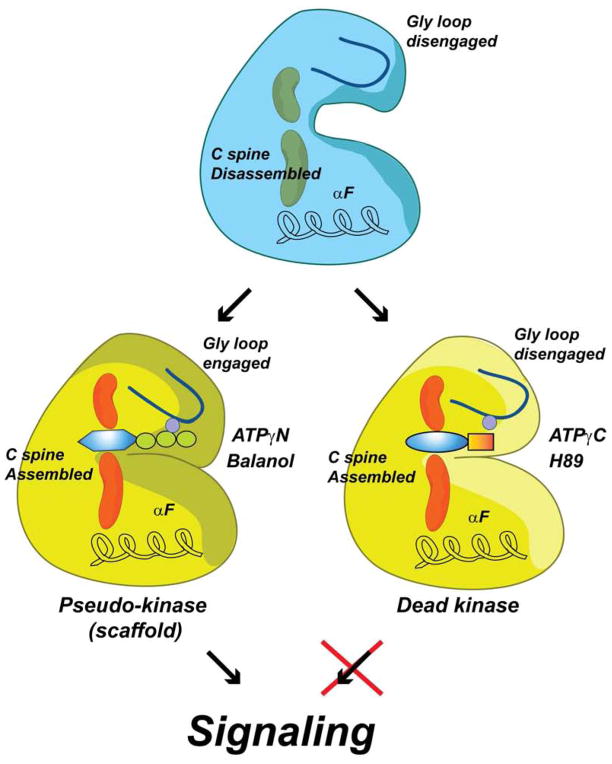
Figure 8. Uncoupling canonical and non-canonical function of kinases.
The apo enzyme (blue) displays both disassembled C spine and disengaged Gly-loop. Binding of non-hydrolyzable ATP analogs or good ATP mimic drug inhibitors (i.e., able to engage Gly-rich loop via coordination of Mg2+ ion) produce a pseudokinase that is unable to carry out phosphoryl transfer but is able to bind substrates cooperatively (yellow). Binding of drug inhibitors that are unable to properly coordinate the Mg2+ ion to engage the Gly-loop (i.e., ATPγC, H89, see also Figure S8) obliterates both catalytic and scaffolding function (dead kinase).