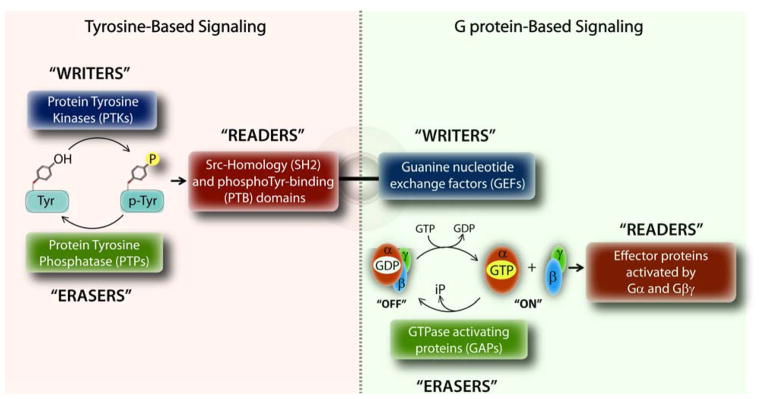
Figure 1. Design principles of tyrosine-based G protein signaling.
Schematic displays the fundamental principles that govern signal transduction within the tyrosine-based (left) and G protein-based (right) signaling pathways. Within each pathway, signals are triggered, propagated or terminated by an independent set of ‘writers’, ‘readers’ and ‘erasers’, respectively. The unusual coexistence of a GEF motif (which triggers G protein signaling) and a SH2-like domain (which propagates tyrosine-based signals) in GIV’s C-terminus allows GIV to trigger G protein signaling in response to tyrosine-based signals. The schematic on the right is adapted after significant modification from Pincus D., et al. (89).